views
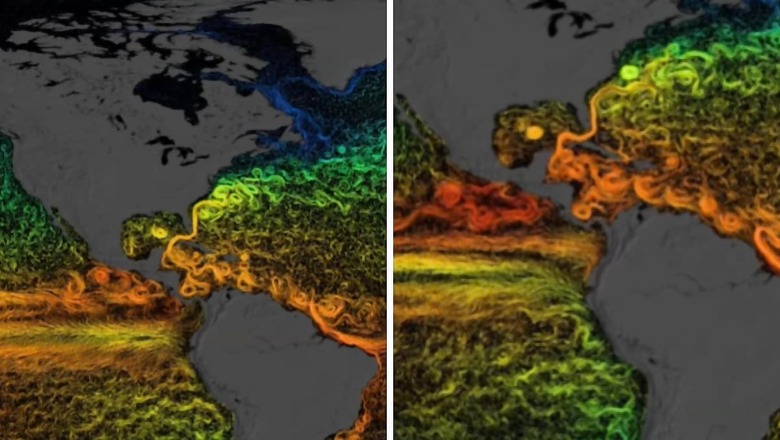
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has released a new visualisation illustrating how human activity is affecting sea surface currents. The graphic shows average ocean current temperatures and their regional differences, using colours like green and blue for cooler temperatures and red, orange and yellow for warmer ones. “Our ocean is changing,” they stated.
“With 70% of the planet covered by water, the seas are important drivers of Earth’s global climate,” the Space Agency wrote in a post on Instagram, pointing out that these changes in ocean currents are happening right “before our eyes” due to increased greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
View this post on Instagram
The post has more than 1 million views on the social media platform.
A user in the comments section wrote, “Climate change is a huge problem.”
“We are changing our oceans, it is not changing by itself,” read another comment. “Scary”, said another user.
Ninety percent of Earth’s warming occurs beneath the ocean’s surface, according to NASA. The ocean’s internal heat has been rising since the start of modern record-keeping in 1955, and this has had a major impact on global warming.
As the ocean heats, thermal expansion—a process where water expands—is triggered by the heat stored there. This process is responsible for one-third to half of the rise in sea levels worldwide.
According to scientists, the upper 700 metres of the ocean are where most of this heat is concentrated.
Based on available data, the ocean has warmed up within the last 10 years more than it has since the 1800s, with 2023 seeing the highest ocean temperatures ever recorded.
The implications of ocean warming are extensive. The increase in sea levels is one of the most obvious effects.
Warmer seas, in addition to accelerating the melting of Earth’s major ice sheets, have led to widespread coral bleaching, significantly impacting marine ecosystems.
According to NASA, as ocean temperatures rise, storms intensify, altering water biochemistry and quality, disrupting food chains and reshaping marine habitats. NASA also points out that El Niño events contribute to increased ocean temperatures.
El Nino occurs when the eastern and central regions of the tropical Pacific Ocean experience warmer-than-usual temperatures. This cyclical warming can amplify temperatures during already hot years, as ocean temperatures play a critical role in influencing global climate patterns.



















Comments
0 comment