views
More than 45 per cent of the over 5.96 lakh COVID-19 tests in Delhi were conducted in the last 16 days, after the government started testing through the rapid-antigen methodology in and around containment zones of the national capital.
Rapid-antigen tests started in the city on June 18.
Since then a total of 2,75,396 tests through the RT-PCR (reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction) and rapid-antigen methods have been conducted in Delhi with around 17,000 tests per day.
Of this, around 1.5 lakh people have been tested through rapid-antigen kits, according to the Delhi government's health bulletins.
Till June 18, health authorities conducted 3,21,302 tests for the disease using the "expensive but gold standard" RT-PCR method.
The number of tests per day has also seen an around four-fold increase from 4,190 tests per day in the first week of June to 15,863 tests per day in the last week of the month.
On Friday alone, more than 24,000 tests -- 10,577 RT-PCR tests and 13,588 rapid-antigen tests -- were conducted in the city, a massive jump from 6,538 tests conducted a month ago on June 3.
In the last one month, from June 3 to July 3, as many as 3.66 lakh people have been tested for COVID-19, which is 12,218 tests daily.
So far, 5,96,698 tests have been conducted through RT-PCR and the rapid-antigen methods.
On Friday, the government expanded rapid-antigen testing, earlier limited to containment zones, to other areas in all 11 districts of the national capital.
Now, state-run and private hospitals in the capital have also begun testing for COVID-19 using this method following the nod of the government.
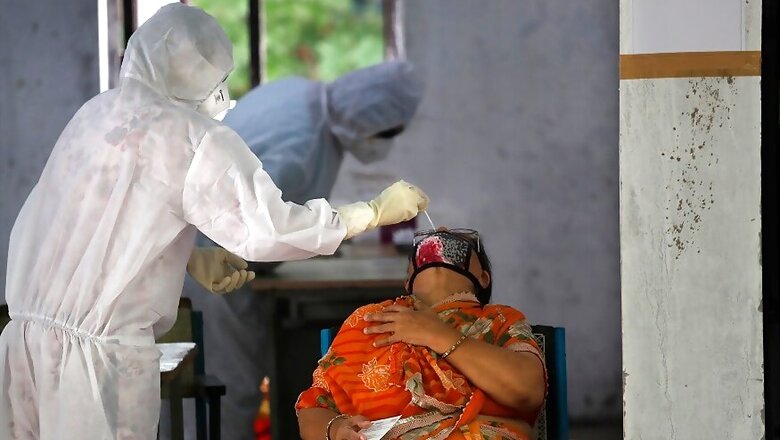
According to health authorities, rapid-antigen testing is an easy and cheaper method as compared to the RT-PCR test .
Each testing kit costs Rs 450 and can provide results within 30 minutes as compared to RT-PCR test that takes three to four hours.
The kits, called Standard Q COVID-19 Ag detection, have been developed by South Korean company S D Biosensor. The testing method involves looking for antibodies which are produced when the body is exposed to a pathogen.
If a person has antibodies associated with novel coronavirus, it means the person is either COVID-19 positive or has recovered.
According to the Indian Council of Medical Research, suspected individuals who test negative for COVID-19 in rapid-antigen test should undergo RT-PCR to rule out the infection.
While positive test results should be considered as true positive and do not need reconfirmation by RT-PCR test, it said.
Rapid-antigen testing requires a prescription and an ICMR form filled by a registered doctor, and a government identity proof, same as that for RT-PCR test.















Comments
0 comment