
views
The racket of adulterating heroin, which was rampant in 2009-10, is once again gaining ground in India, especially in the north and north-eastern states, say officials. The main reason for modifying one of the most expensive drugs is to sell it cheaper and make more profit.
Though no big illegal factories have been traced in recent years, there have been instances noticed of adulterating heroin at very small levels. Experts and officials say that adulterated heroin is more harmful than the pure form as it damages organs more quickly.
This week, the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) raided a small-level factory of manufacturing/adulterating heroin in the capital.
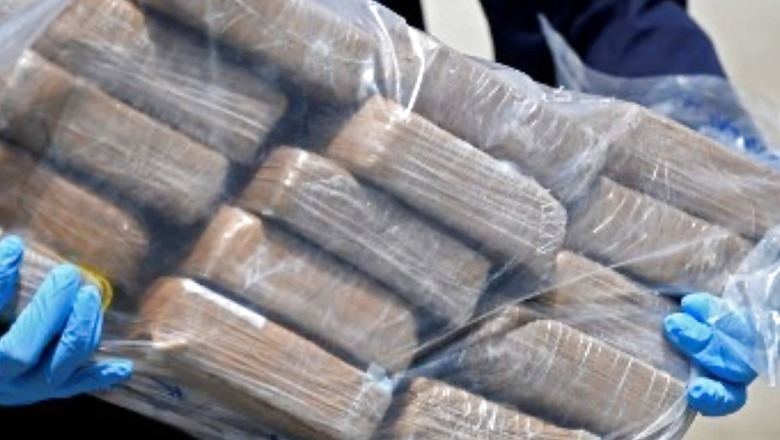
“In one of the biggest hauls in recent times, Narcotics Control Bureau Delhi Zone seized 50 kg high-quality heroin, 47 kg suspected narcotics, Rs 30 lakh drug money in cash, cash counting machines and other incriminating material from residential premises in Jamia Nagar, Shaheen Bagh on 27.04.22 on a tip-off. The contraband was stored in travel bags, backpacks and jute bags,” the NCB said.
The anti-drugs agency also said that these syndicates have expertise in manufacturing/adulterating heroin locally.
The seized heroin originated from Afghanistan and the drug money is suspected to be channelled through hawala, say officials.
But this is not the only such case in recent months. In December, the Assam Rifles along with Manipur police seized 54 kg of adulterated heroin packed in soap cases. The recovery was done from a warehouse that was under surveillance.
Local officials said that the gang was adulterating heroin with the help of a Myanmar-based link.
Manufacturing heroin is a complex process, NCB officials say, and requires expertise.
“It requires a good amount of knowledge and infrastructure along with large spaces to store opium poppy which is the main source of heroin. In our recent case, we suspect that they were adulterating heroin that had arrived from Afghanistan. Here in Delhi’s Shaheen Bagh, the accused used to extract heroin from the goods that were used to hide it,” a senior NCB official said.
Former Punjab director general of police (DGP) Shashi Kant, known for his crackdown on drugs in the state, says that manufacturing of heroin is never seen in large quantities.
“Why does anyone need to manufacture heroin in India when smugglers are getting enough supply of one of the best qualities of it. In India, as far as I know, there is no big illegal manufacturing unit of heroin, though adulterated heroin is back once again. Reports suggest that various parts of India have small units where smugglers mix and adulterate heroin to sell it at a cheaper price, but this type of adulterated heroin damages the body much faster,” Shashi Kant told News18.
Down to the root
India is among very few countries producing opium legally for medical and scientific purposes for domestic needs. Heroin is manufactured after processing opium, so it is important for the government to keep a very strict check on opium production. The central government notifies the general conditions for the grant of licence specified for the cultivation of opium poppy every year.
Opium poppy is cultivated in three states of India: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh. There have been cases though where opium was cultivated illegally. But there is hardly any evidence that opium was used to produce heroin in large quantities.
However, around 1999 to 2004, agencies detected some heroin manufacturing labs in the country. As per the government data, the number of heroin manufacturing facilities (labs) detected during 1999 was three, which doubled by 2002 but had dropped back to three again by 2003.
But now there is hardly any illegal manufacturing facility as there is a plentiful supply of the best quality of heroin in India from Afghanistan and Pakistan, an NCB official said.
A United Nations report says Afghanistan produces 85% of the world’s opium and it suspects that the country’s harvest will account for more than 90% of worldwide illegal heroin production. So India is not a manufacturer but a consumer of heroin, the NCB official said.
From opium to morphine to heroin
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, the first step of manufacturing opium starts with crushing raw opium, mixing and suffusing it with hot water. Further, calcium oxide is mixed with raw opium and left for hours. This is the first step of extracting morphine from raw opium. The next step requires precipitation, isolation and drying of the morphine, which needs basic machines.
Officials dealing with narcotics cases said that the process requires few machines but is a days-long exercise. After drying the morphine, manufacturers add two chemicals and the first version of heroin is ready, which is also known as brown sugar because of its colour.
But to get grade 3 heroin, the brown powder requires two more steps involving four chemicals including ammonia. These processes also increase the product’s pH level to 12 from eight. The whole process needs a specific quantity of eight chemicals and activated carbon, and is an intricate process.
Read all the Latest India News here
















Comments
0 comment