
views
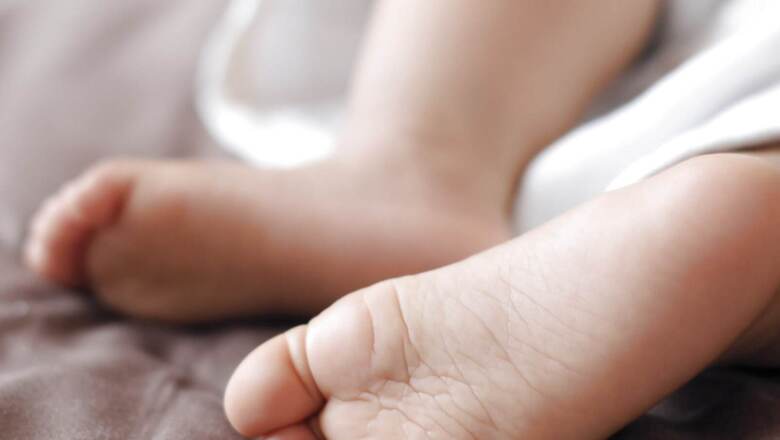
India is one of the most populated countries in the world, with a lot of demographic, social, and economic disparity among its people. Many babies in India are born with disorders. While many survive, some lose their lives. One such disorder putting a load on the lives of people is thalassemia. This is a genetic blood disorder. In this condition, the haemoglobin level is less than normal, which damages the red blood cells. Red blood cells are essential for carrying oxygen to the cells. The absence of healthy red blood cells in the body makes a person feel tired and short of breath. This gives rise to the underlying condition of anaemia. Severe anaemia can even lead to death. Let’s look at the symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thalassemia depend on the type and severity of the condition. If someone has thalassemia, then they can have more than one of the following symptoms.
- Extreme tiredness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Yellowish skin
- Deformities in the facial bone
- Slow growth
- Swelling in abdomen
- Dark-coloured urine
Causes
The genetic disorder is caused by a mutation in the DNA of cells that make haemoglobin. As DNA is affected, it passes from parents to children. Hemoglobin is a protein made of molecular chains, alpha and beta. There are two types of thalassemia, Alpha-thalassemia and Beta-thalassemia. If the alpha molecule gets mutated, it causes alpha-thalassemia, and the severity of the condition depends on the number of mutations. The more mutations, the more severe thalassemia is.
On the other hand, beta-thalassemia affects the beta chain of molecules. The number of mutations does not matter, but the area that is being affected determines the severity of beta-thalassemia.
Diagnosis and treatment
As thalassemia is genetic, it can’t be prevented. If parents have the disease, they’ll pass it on to their children. Thalassemia can be diagnosed only during pregnancy. There is an advanced form of assisted reproduction that can test for gene mutations in an embryo while it is still in its early stages.
Apart from this, most children show moderate to severe symptoms within two years of birth, which can be confirmed using a blood test. In the early stages, treatment is not required, whereas for severe patients, doctors often suggest treatment after looking at the condition. The common treatments are blood transfusions, chelation therapy, and stem cell transplants.
Read all the Latest Lifestyle News here
















Comments
0 comment