Amazon, Giver of Life, Unleashes the Pandemic, Shows There’s No Such Thing as ‘Isolated’ Communities

views
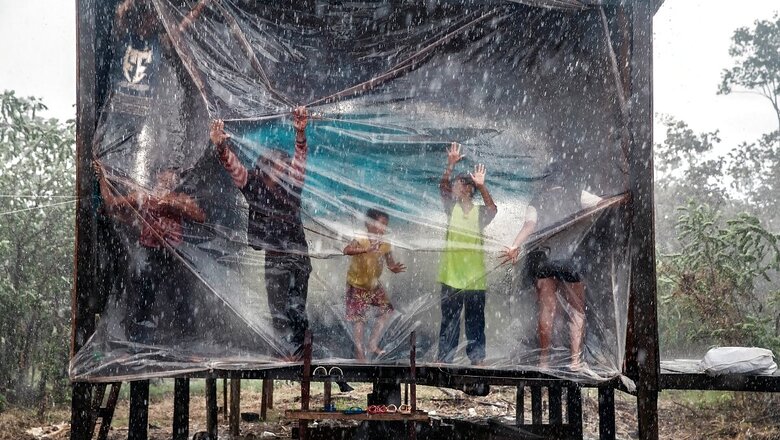
The virus swept through the region like past plagues that have traveled the river with colonizers and corporations.
It spread with the dugout canoes carrying families from town to town, the fishing dinghies with rattling engines, the ferries moving goods for hundreds of miles, packed with passengers sleeping in hammocks, side by side, for days at a time.
The Amazon River is South America’s essential life source, a glittering superhighway that cuts through the continent. It is the central artery in a vast network of tributaries that sustains some 30 million people across eight countries, moving supplies, people and industry deep into forested regions often untouched by road.
But once again, in a painful echo of history, it is also bringing disease.
As the pandemic assails Brazil, overwhelming it with more than 2 million infections and more than 84,000 deaths — second only to the United States — the virus is taking an exceptionally high toll on the Amazon region and the people who have depended on its abundance for generations.
In Brazil, the six cities with the highest coronavirus exposure are all on the Amazon River, according to an expansive new study from Brazilian researchers that measured antibodies in the population.
The epidemic has spread so quickly and thoroughly along the river that in remote fishing and farming communities like Tefé, people have been as likely to get the virus as in New York City, home to one of the world’s worst outbreaks.
“It was all very fast,” said Isabel Delgado, 34, whose father, Felicindo, died of the virus shortly after falling ill in the small city of Coari. He had been born on the river, raised his family by it and built his life crafting furniture from the timber on its banks.
In the past four months, as the epidemic traveled from the biggest city in the Brazilian Amazon, Manaus, with its high-rises and factories, to tiny, seemingly isolated villages deep in the interior, the fragile health care system has buckled under the onslaught. Cities and towns along the river have some of the highest deaths per capita in the country — often several times the national average.
Tyler Hicks, a photographer for The New York Times, spent weeks on the river, documenting the spread of the virus. In Manaus, there were periods when every COVID ward was full and 100 people were dying a day, pushing the city to cut new burial grounds out of thick forest. Grave diggers lay rows of coffins in long trenches carved in the freshly turned earth.
Down the river, hammocks have become stretchers, carrying the sick from communities with no doctors to boat ambulances that careen through the water. In remote reaches of the river basin, medevac planes land in tiny airstrips sliced into the lush landscape only to find that their patients died while waiting for help.
The virus is exacting an especially high toll on Indigenous people, a parallel to the past. Since the 1500s, waves of explorers have traveled the river, seeking gold, land and converts — and later, rubber, a resource that helped fuel the Industrial Revolution, changing the world. But with them, these outsiders brought violence and diseases like smallpox and measles, killing millions and wiping out entire communities.
“This is a place that has generated so much wealth for others,” said Charles C. Mann, a journalist who has written extensively on the history of the Americas, “and look at what’s happening to it.”
Indigenous people have been roughly six times as likely to be infected with the coronavirus as white people, according to the Brazilian study, and are dying in far-flung river villages untouched by electricity.
Even in the best of times, the Amazon was among the most neglected parts of the country, a place where the hand of the government can feel distant, even nonexistent.
But the region’s ability to confront the virus has been further weakened under President Jair Bolsonaro, whose public dismissals of the epidemic have verged at times on mockery, even though he has tested positive himself.
The virus has surged on his government’s disorganized and lackluster watch, tearing through the nation. From his first days in office, Bolsonaro has made it clear that protecting the welfare of Indigenous communities was not his priority, cutting their funding, whittling away at their protections and encouraging illegal encroachments into their territory.
To the outsider, the thickly forested region along the Amazon River appears impenetrable, disconnected from the rest of the world.
But that isolation is deceptive, said Tatiana Schor, a Brazilian geography professor who lives off one of the river’s tributaries.
“There is no such thing as isolated communities in the Amazon,” she said, “and the virus has shown that.”
The boats that nearly everyone relies on, sometimes crowded with more than 100 passengers for many days, are behind the spread of the virus, researchers say. And even as local governments have officially limited travel, people have continued to take to the water because almost everything — food, medicine, even the trip to the capital to pick up emergency aid — depends on the river.
Scholars have long referred to life on the Amazon as an “amphibious way of being.”
The crisis in the Brazilian Amazon began in Manaus, a city of 2.2 million that has risen out of the forest in a jarring eruption of concrete and glass, tapering at its edges to clusters of wooden homes perched on stilts, high above the water.
Manaus, the capital of Amazonas state, is now an industrial powerhouse, a major producer of motorcycles, with many foreign businesses. It is intimately connected to the rest of the world — its international airport sees about 250,000 passengers a month — and, through the river, to much of the Amazon region.
Manaus’ first documented case, confirmed on March 13, came from England. The patient had mild symptoms and quarantined at home, in a wealthier part of town, according to city health officials.
Soon, though, the virus seemed to be everywhere.
“We didn’t have any more beds — or even armchairs,” Dr. Álvaro Queiroz, 26, said of the days when his public hospital in Manaus was completely full. “People never stopped coming.”
Gertrude Ferreira Dos Santos lived on the city’s eastern edge, in a neighborhood pressed against the water. She used to say that her favorite thing in the world was to travel the river by boat. With the breeze on her face, she said, she felt free.
Then, in May, dos Santos, 54, fell ill. Days later, she called her children to her bed, making them promise to stick together. She seemed to know that she was about to die.
Eduany, 22, her youngest daughter, stayed with her that night. In early morning, as Eduany got up to take a break, her sister Elen, 28, begged her to come back.
Their mother had stopped breathing. The sisters, in desperation, attempted mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. At 6 a.m., the sun rising above the city, dos Santos died in their arms.
When men in white protective suits arrived later to carry away her body, the sisters began to wail.
Dos Santos had been a single mother. Life had not always been easy. But she had maintained a sense of wonder, something her daughters admired. “In everything she did,” Elen said, “she was joyful.”
Her mother’s death certificate listed many underlying conditions, including long-standing breathing problems, according to the women. It also listed respiratory failure, a key indicator that a person has died of the coronavirus.
But her daughters didn’t believe she was a victim of the pandemic. She had certainly died of other causes, they said. God would not have given her such an ugly disease.
Along the river, people said similar things over and over, reluctant to admit to possible contagion, even as the health of their siblings and parents declined. Many seemed to think their families would be shunned, that a diagnosis would somehow tarnish an otherwise dignified life.
But as this stigma led people to play down symptoms of the virus out of fear, doctors said, the pandemic was spreading quickly.
After Manaus, the virus traveled east and west, racing away from the region’s health care center.
In Manacapuru, more than an hour from the capital, Messias Nascimento Farias, 40, carried his ailing wife to their car and sped down one of the region’s few country roads to meet the ambulance that could carry her to a hospital.
His wife, Sandra Machado Dutra, 36, gasped in his truck.
“The Lord is my shepherd, I shall not want,” he prayed over and over until he handed her to health care workers. They were lucky. She survived.
But for most people living along the river, hundreds of boat miles from Manaus, the fastest way to a major hospital is by plane.
Even before the virus arrived, people in far-flung communities with a life-threatening emergency could make a frantic call for an airplane ambulance that would take them to a hospital in the capital.
But the small planes turned out to be dangerous for people with COVID-19, sometimes causing blood oxygen levels to plummet as the aircraft rose. Very few of the airlift patients seemed to be surviving, doctors said.
Instead, physicians and nurses found themselves flying their patients to painful deaths far from everything and everyone they had loved.
One morning in May, a white plane touched down at the airport in Coari, about 230 miles from Manaus.
On the tarmac on a stretcher was Delgado, 68, the furniture maker, barefoot and barely breathing.
Dr. Daniel Sérgio Siqueira and a nurse, Walci Frank, exhausted after weeks of constant work, loaded him into the small cabin. As the plane rose, his oxygen levels began to dive.
Delgado’s daughter Isabel turned to the doctor in a panic. “My father is very strong,” she told him. “He is going to make it.”
When the Delgados finally reached the hospital in Manaus, Isabel was stunned by the scenes around her. Despairing relatives held up loved ones who had crumpled under the burden of disease, hurrying them in for treatment.
At the same time, patients who had managed to survive COVID-19 staggered out, into the jubilant arms of family and friends.
“I was just there,” she said, “praying that God would save my father.”
Delgado died a few days later. When Isabel found out, the doctor started crying with her.
She had no doubt that the river her father loved had also brought him the virus. Soon, she and five other family members fell ill, too.
When the coronavirus arrived in the Americas, there was widespread fear that it would take a devastating toll on Indigenous communities across the region.
In many places along the Amazon River, those fears appear to be coming true.
At least 570 Indigenous people in Brazil have died of the disease since March, according to an association that represents the country’s Indigenous people. The vast majority of those deaths were in places connected to the river.
More than 18,000 Indigenous people have been infected. Community leaders have reported entire villages confined to their hammocks, struggling to rise even to feed their children.
In many instances, the very health workers sent to help them have inadvertently spread the virus.
In the riverside hamlet of São José da Fortaleza, Chief Iakonero Apurinã’s relatives sent word, one by one, that they couldn’t eat, that they heard voices, that they were too sick to get up.
Soon, it seemed to the chief that everyone in her community was sick.
Apurinã, 54, said her group of 35 Apurinã families had survived generations of violence and forced labor. They had arrived in São José da Fortaleza decades ago, believing that they would finally be safe.
It was the river, said the chief, that had sustained them, feeding, washing and cleansing them spiritually.
Then the new disease came, and the chief was ferrying traditional teas from home to home. Soon came her own cough and exhaustion. A test in Coari confirmed that she had caught the virus.
Apurinã didn’t blame the river. She blamed the people who traveled it.
“The river to us is purification,” she said. “It’s the most beautiful thing there is.”
Miraculously, she said in mid-July, not a single person among the 35 families had died.
In Tefé, a city of 60,000 people nearly 400 miles along the river from Manaus, the virus had arrived with gale force.
At the small public hospital, where officials initially planned to accommodate 12 patients, nearly 50 crowded the makeshift COVID-19 unit. Dr. Laura Crivellari, 31, the hospital’s only infectious disease expert, took them in, doing what she could with two respirators, no intensive care unit, many sick colleagues — and no one to replace them.
At one of the worst moments, she was the only physician on duty for two days, overseeing dozens of critically ill patients.
The constant death pushed Crivellari to her breaking point. Some days she barely stopped to eat or drink.
At home, she shared her anguish with her partner. She was thinking of giving up medicine, she said. “I can’t carry on like this,” she told him.
The pandemic has been brutal on medical workers around the world, and it has been particularly difficult for the doctors and nurses navigating the vast distances, frequent communication cuts and deep supply scarcity along the Amazon.
Without proper training or equipment, many nurses and doctors along the river have died. Others have infected their families.
Crivellari knew her city was vulnerable. It’s a three-day boat ride from Manaus to Tefé, with ferries often carrying 150 people at a time.
“Our fear was that an infected person would contaminate the whole boat,” she said, “and that’s what ended up happening.”
By early July, the daily deaths in Tefé were dropping, and Crivellari began to celebrate the patients she had been able to save. She no longer thinks of quitting medicine.
Tefé, as a whole, took a cautious collective breath.
The virus, at least for the moment, had moved to a new place on the river.
Julie Turkewitz and Manuela Andreoni c.2020 The New York Times Company
















Comments
0 comment