
views
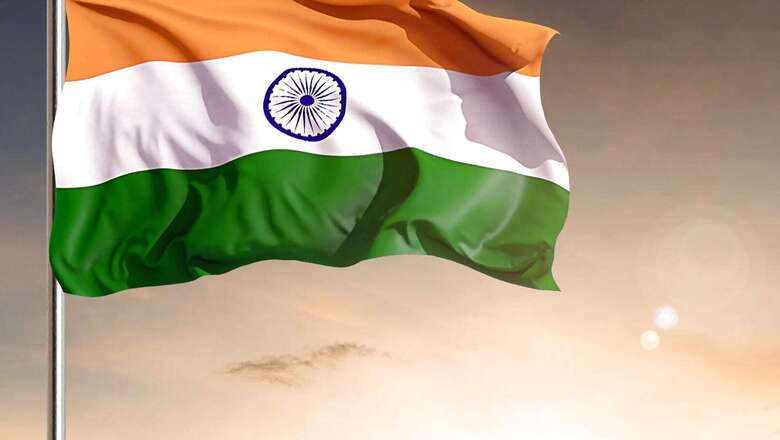
India celebrated its 74th Republic Day on January 26, 2023. A country of 140 crores with a diverse population of different ethnicities, cultures, and regional identities, with their own set of issues and preferences, set Indian Constitution is a point of juncture to address the issues that directly affect the people in India.
India observes Republic Day as it marks the date – January 26, 1950 – on which the constitution came into effect. It established India as a ‘republic’, separate from British rule, as it replaced the Government of India Act 1935 with that of the Constitution of India.
The making of the Indian constitution is a phenomenal story of the great minds of India coming together to give a geographical region a national identity. It was initiated in the constituent assembly and the elected members brainstormed to give space to the diverse nature of India.
Today in Classes With News18, we bring to you the history of the constitution of India and how it was drafted.
Making of the Indian constitution
The discussion about the making of the Indian constitution opens up with a detailed explanation of the democratic constitution which was formulated in South Africa. The resentment of the Black community in South Africa against Apartheid laid the foundation for the Democratic Constitution of South Africa. India’s Constitution was drawn up under very difficult circumstances. The country was born through a partition on the basis of religious differences and was a traumatic experience for the people of India and Pakistan. The British had left it to the rulers of the princely states to decide whether they wanted to merge with India or with Pakistan or remain independent. The merger of these princely states was a difficult and uncertain task. When the constitution was written, the future of the country did not look as secure as it does today.
Read | Learn All About India and Pakistan Partition in Classes With News18
Path to the Indian Constitution
While the work of drafting the constitution of India was going on, the idea of what democratic India should look like was constantly evolving during the freedom struggle. In 1928, Motilal Nehru and eight other Congress leaders drafted a constitution for India and In 1931, the resolution at the Karachi session of the Indian National Congress dwelt on how independent India’s constitution should look. These documents contained essential mentions like the Right to Freedom and Equality, Universal Adult Franchise along with rights that were stated to protect the minorities in India. These basic values were accepted by all leaders much before the Constituent Assembly met to deliberate on the Constitution. Thus, it was seen that the Indian constitution accepted many vital details as well as procedures from Indian laws such as the Government of India Act 1935. Many of our leaders were inspired by the ideals of the French Revolution, the practice of parliamentary democracy in Britain, and the Bill of Rights in the US.
The Constituent Assembly
The drafting of the constitution was done by an assembly of elected representatives called the Constituent Assembly. Elected members brainstormed to give space to the diverse nature of India. Elections to the Constituent Assembly were held in July 1946 and its first meeting was held in December 1946. Soon after, the country was divided into India and Pakistan and the Constituent Assembly was also divided into the Constituent Assembly of India and of Pakistan. The Constituent Assembly that wrote the Indian constitution had 299 members. The Assembly adopted the Constitution on November 26, 1949 but it came into effect on January 26, 1950. To mark this day we celebrate January 26 as Republic Day every year.
First, some basic principles were decided and agreed upon. Then a Drafting Committee chaired by Dr B.R. Ambedkar prepared a draft constitution for discussion. Along with him, the other members of the Drafting Committee were Mohammad Saadulla, Alladi Krishnaswami Ayyar, N. Gopalaswami, B.L. Mitter, to name a few. They contributed their expertise in formulating the quintessential constituents of the Indian Constitution. Several rounds of thorough discussion took place on the Draft Constitution, clause by clause. More than two thousand amendments were considered. Every document was presented and every word spoken in the Constituent Assembly has been recorded and preserved.
The making of the Indian constitution was carried out by a well-versed team with expertise in law, rules, and regulations as well as an in-depth understanding of the history, philosophy, and diverse culture of India. Their understanding of India was of an ancient civilisation that needed a new code of conduct, with justice and equality as the primary goal. The vision of Mahatma Gandhi and its opposition by Dr Ambedkar can be considered the key to the question of justice and equality in India.
Philosophy of the Constitution
It is important to remember that the making of the Indian Constitution was preceded by its philosophy which was constituted under the Preamble to the Constitution of India. The Preamble includes certain principles that guide governance and law in India. All the noble ideals of our founding fathers are reflected through the preamble of the constitution. The preamble gives us a sense of togetherness and tells us what we have chosen for ourselves as a nation in a very poetic manner.
Institutional Design
A constitution is not merely a statement of values and philosophy. It is mainly about embodying these values into institutional arrangements. It is a very long and detailed document. Therefore, it needs to be amended quite regularly to keep it updated. Provisions are made to incorporate changes, known as constitutional amendments from time to time. Like any Constitution, the Indian Constitution also lays down a procedure for choosing persons to govern the country. It defines who will have how much power to make which decisions. And it puts limits to what the government can do by providing some rights to the citizen that cannot be violated.
To learn about other topics taught in school, explained by News18, here is a list of other Classes With News18: Queries Related to Chapters on Elections | Sex Versus Gender | Cryptocurrencies | Economy & Banks | How to Become President of India | Post Independence Struggle | How India Adopted Its Flag | Formation of States & United India | Tipu Sultan | Indian Teachers Day Different from Rest of the World |Queen Elizabeth & Colonialism | Challenges of Democracy | Print Culture | India and Pakistan Partition |
Read all the Latest Education News here
















Comments
0 comment