
views
Every year on February 2, World Wetlands Day (WWD) highlights the crucial role these ecosystems play in our lives and the health of our planet. This year’s theme, “Wetlands and Human Wellbeing,” underscores the deep connection between the well-being of wetlands and our own. These vital freshwater havens support over 100,000 species, forming the foundation for our existence. They provide sustenance for billions, with rice grown in wetland paddies forming a staple food for 3 billion people and contributing 20% of global food production.
Beyond food, wetlands act as nature’s shock absorbers, softening the impact of rainfall and reducing the risk of floods and storm surges.
Recognizing their invaluable role, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) actively supports the conservation, restoration, and sustainable management of wetlands. This work focuses on food security and agriculture, encompassing crop and livestock production, forestry, fisheries, and aquaculture. Additionally, the FAO promotes integrated land and water resources management, addressing challenges posed by climate change, biodiversity loss, and competing demands.
WORLD WETLANDS DAY HISTORY
World Wetlands Day traces its roots back to 1971. Born from the Ramsar Convention, officially known as the Convention on Wetlands, this day serves as a powerful reminder of the critical role wetlands play in our world. India is one of the Contracting Parties to Ramsar Convention, signed in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971. India ratified this Convention on 1 February, 1982.
The date itself holds significant meaning, marking the anniversary of the Convention’s adoption in Ramsar, Iran. This landmark agreement established a framework for the international conservation and wise use of wetlands.
Earlier in August 2022, India achieved a significant milestone of taking the total number of Ramsar Sites to 75 during the 75th Year of Independence. Due to a significant policy push from the Government of India, the number of Ramsar sites has increased from 26 to 80 in the last ten years, of which 38 have been added in the last three years alone.

5 NEW RAMSAR SITES IN INDIA
India’s commitment to wetland conservation takes a step forward with the addition of five new Ramsar sites, bringing the total to 80! On the eve of World Wetlands Day 2024, Union Minister Bhupender Yadav announced this positive development, highlighting the government’s growing focus on environmental protection under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership.
Powered by 5!Met with Dr Musonda Mumba, Secretary General of the Convention on Wetlands, in Delhi today.
With two days to go for #WorldWetlandsDay, India today increased its tally of Ramsar Sites from 75 to 80.
The emphasis PM Shri @narendramodi ji has put on environmental… pic.twitter.com/g1aMX8mS9V
— Bhupender Yadav (@byadavbjp) January 31, 2024
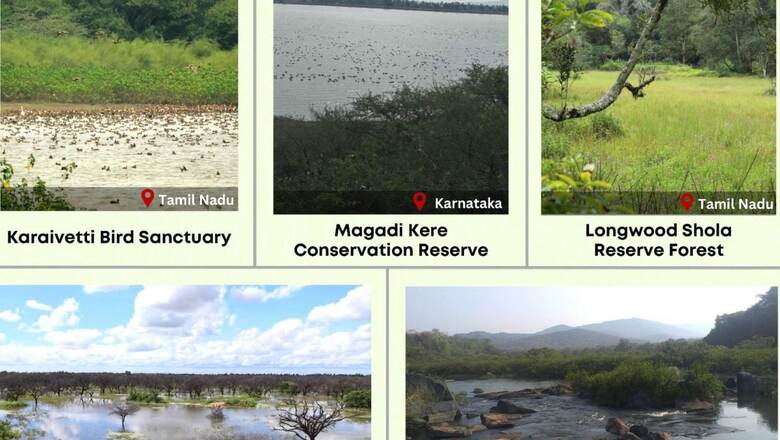
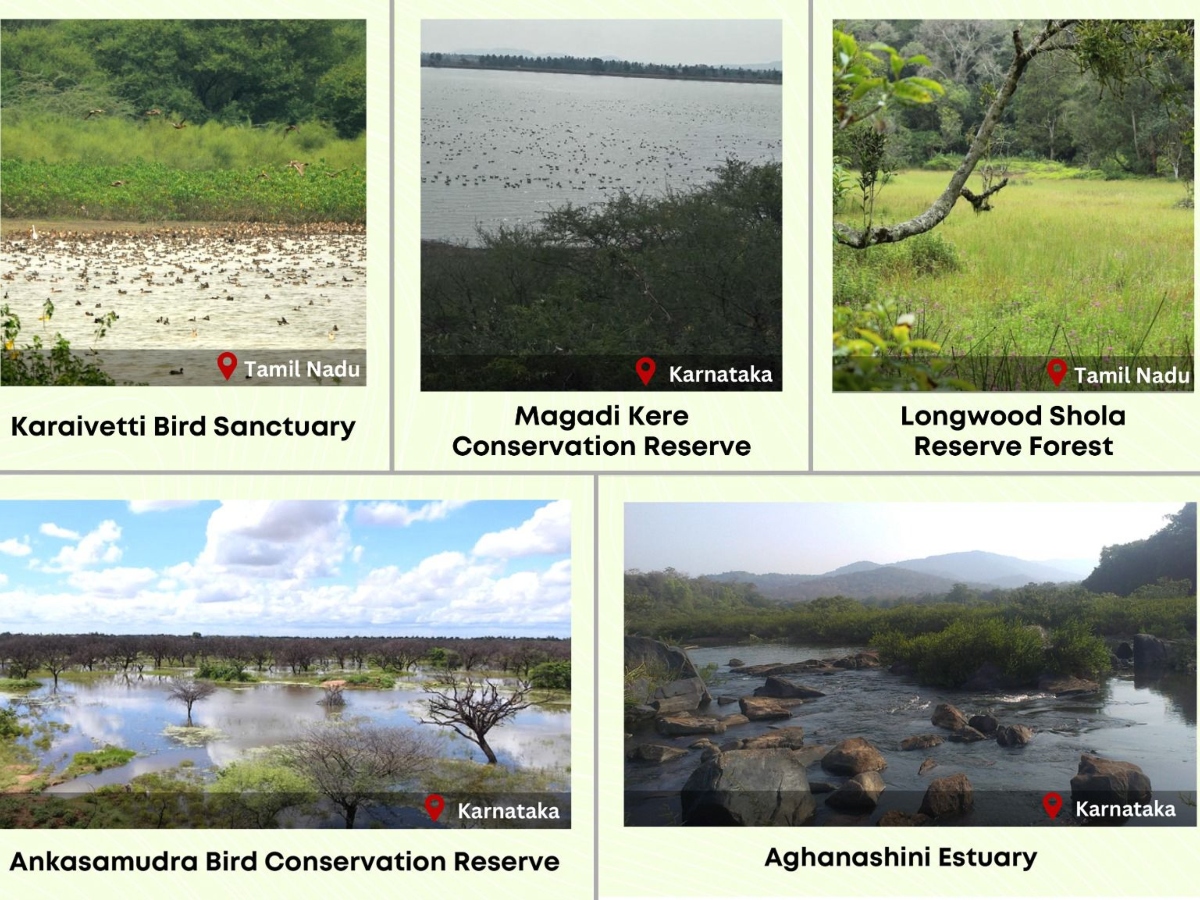
These five new sites, spanning across Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, join the prestigious list of Wetlands of International Importance.
Three sites – Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve, Aghanashini Estuary, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve – contribute to Karnataka’s wetland diversity, while Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest add to Tamil Nadu’s already impressive list of 16 Ramsar sites, the highest in India.
This expansion adds over 5,500 hectares to the protected area under Ramsar, bringing the total to 1.33 million hectares. This marks a significant step towards safeguarding vital ecosystems that support rich biodiversity and provide essential services to communities.
Yadav commended the states of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka for their efforts in wetland conservation. He also emphasized the Amrit Dharohar initiative, emphasizing the government’s commitment to preserving India’s natural heritage.
RAMSAR LIST FAQs
What Is Ramsar List?
The Ramsar List is a collection of Wetlands of International Importance designated under the Ramsar Convention. This intergovernmental treaty, signed in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran, aims to conserve wetlands and promote their wise use.
What qualifies a wetland for the list?
It must be a wetland site of international importance due to its:
- Ecological, botanical, zoological, limnological, or hydrological importance.
- Value for waterfowl, especially as waterbird habitat.
It must meet at least one of the nine specific criteria laid out in the Ramsar Convention.
What’s the significance of being on the list?
- Countries commit to conserving and wisely using the wetland.
- International attention is drawn to the site, raising awareness and potentially providing resources for conservation efforts.
- The site becomes part of a global network of protected wetlands, promoting international cooperation and knowledge sharing.
Current status of the Ramsar List:
As of November 2023, there are over 2,500 Ramsar sites around the world, protecting over 257 million hectares.
172 countries are signatories to the Ramsar Convention.
India’s involvement:
- India currently has 80 Ramsar sites, covering over 1.33 million hectares.
- This makes India the country with the fourth highest number of Ramsar sites globally.
- Five new sites were recently added to the list in celebration of World Wetlands Day 2024.

















Comments
0 comment