
285
views
views
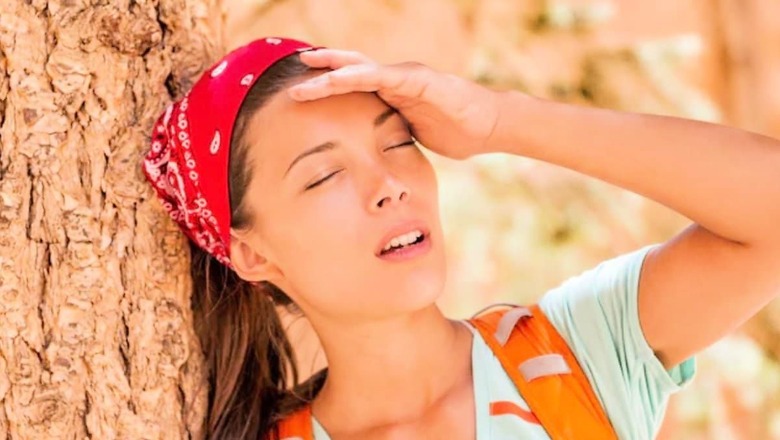
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of dehydration is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing potential complications.
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. This can lead to an imbalance in essential minerals and electrolytes, disrupting normal bodily functions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of dehydration is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing potential complications.
Causes of Dehydration:
- Inadequate Fluid IntakeNot drinking enough fluids, especially in hot weather or during physical activity, can lead to dehydration.
- Excessive SweatingIntense physical activity, fever, or hot weather can cause excessive sweating, leading to fluid loss.
- Diarrhea and VomitingFluid loss through diarrhea and vomiting can quickly deplete the body of essential fluids and electrolytes.
- Frequent UrinationCertain medical conditions or medications can cause increased urination, leading to fluid loss.
- Alcohol and Caffeine ConsumptionBoth alcohol and caffeine have diuretic effects, increasing urine production and contributing to dehydration.
- IllnessCertain illnesses such as diabetes, kidney disease, and infections can increase the risk of dehydration.
Symptoms of Dehydration:
- ThirstFeeling thirsty is the body’s first signal of dehydration.
- Dry Mouth and LipsDry mouth and cracked lips are common symptoms of mild dehydration.
- Dark UrineDark yellow urine indicates concentrated urine due to dehydration.
- FatigueDehydration can cause fatigue and dizziness due to reduced blood volume and oxygen delivery to cells.
- HeadacheDehydration can lead to headaches and migraines.
- Muscle CrampsElectrolyte imbalances resulting from dehydration can cause muscle cramps.
- ConfusionSevere dehydration can affect cognitive function and lead to confusion and irritability.
- Sunken EyesIn infants and young children, sunken eyes may indicate dehydration.
Prevention of Dehydration:
- Stay HydratedDrink plenty of fluids throughout the day, especially water. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily, but this may vary depending on individual needs and activity levels.
- Monitor Urine ColorCheck the color of your urine. Pale yellow or clear urine indicates adequate hydration, while dark yellow urine suggests dehydration.
- Rehydrate After Exercise:Drink water before, during, and after exercise to replace fluids lost through sweating.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine:Reduce consumption of alcoholic and caffeinated beverages, as they can contribute to dehydration.
- Eat Hydrating Foods:Consume foods with high water content, such as fruits and vegetables, to supplement fluid intake.
- Be Mindful of Medications:Some medications can increase the risk of dehydration. Consult your healthcare provider about managing fluid intake while taking medication.
- Take Breaks in Hot Weather:If exposed to hot weather, take regular breaks in shaded or cool areas and drink plenty of fluids.
- Monitor Fluid Losses:Pay attention to fluid losses through sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea, and replenish fluids accordingly.By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for dehydration, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal hydration levels and promote overall health and well-being.
















Comments
0 comment