
views
From the Mars Orbiter Spacecraft completing its one year around the Mars orbit, to launching India’s first multi-wavelength Observatory in Space, the Department of Space has had several pathbreaking achievements up its sleeves in the year 2015.
Following are the significant achievements and details of the Innovative Programmes launched by the Department of Space during the year 2015:
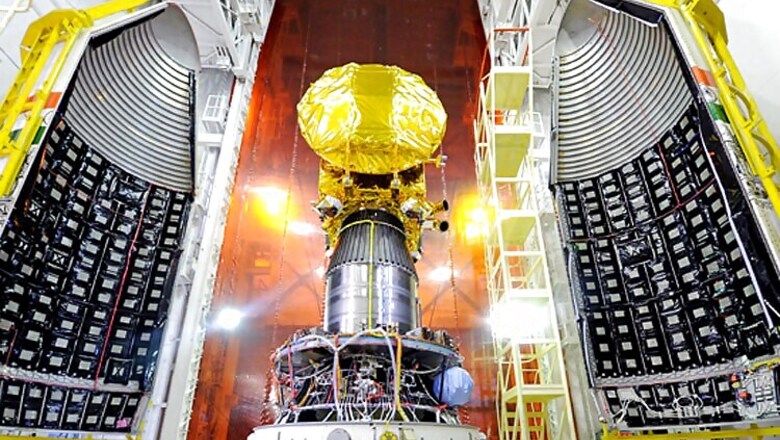
1. MARS Orbiter Mission:
India's Mars Orbiter Spacecraft successfully completed its mission objective as planned and completed one year around Mars orbit on September 24, 2015. It was successfully placed into an elliptical orbit around planet Mars on September 24, 2014. The Spacecraft is in good health and all the five scientific payloads are providing valuable data about the Mars surface features and Martian atmosphere. The increased duration of observation of Mars by five scientific payloads beyond the designed life of six months is enabling enhanced coverage of Mars in different seasons. A book titled ‘From Fishing Hamlet to Red Planet’, India’s space Journey, with series of articles from luminaries from ISRO, was released on November 5, 2015, on the second anniversary of Mars Orbiter spacecraft launch.
By successfully placing Mars Orbiter Spacecraft around Mars, ISRO has become the fourth space agency to successfully send a spacecraft to Mars orbit and India became the first country in the world to do so in its first attempt. The Mission has been awarded “Space Pioneer Award” for science and engineering category for the year 2015 by the US based National Space Society. The Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development has been awarded to ISRO in recognition of its path-breaking.
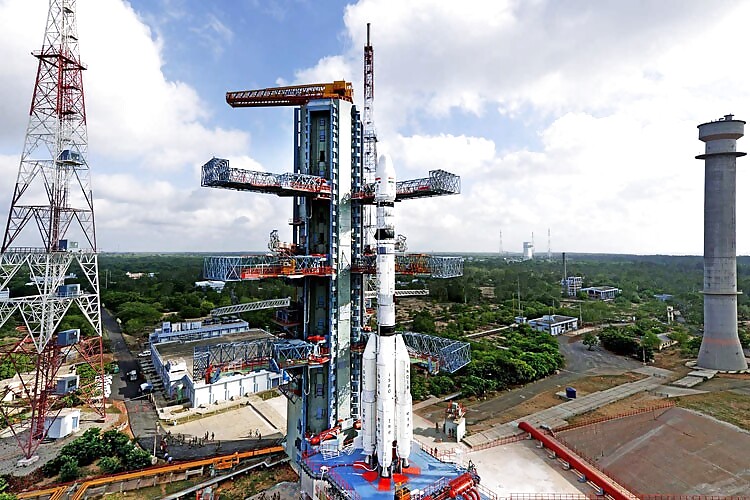

2. Successful launch of GSLV with Indigenous Cryogenic Stage:
On August 27, 2015, Geo-Synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-D6), equipped with the indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS), successfully launched GSAT-6, the country's advanced communication satellite, into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). This was the second consecutively successful flight of GSLV with the indigenous CUS, which underscores the success of ISRO in mastering the highly complex cryogenic rocket propulsion technology. This launch also signifies a major step forward in achieving the self reliance in launching 2 Ton class communication satellites into GTO.
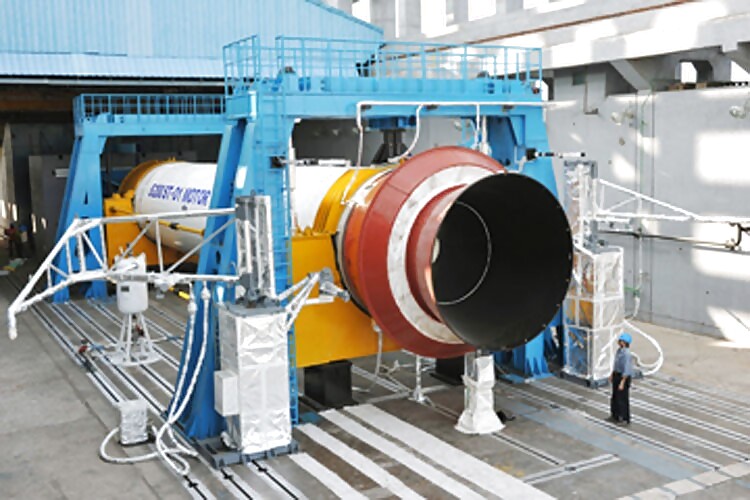

3. Development of Next Generation Geo-Synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III:
The first experimental flight of heavy lift next generation launch vehicle, GSLV-Mk III, was successfully conducted on December 18, 2014 from Sriharikota. This flight has validated the complex atmospheric regime of flight and demonstrated the Integrity of design of GSLV Mk III.
This engine will be used for powering the Cryogenic stage (C25) of GSLV Mk-III launch vehicle. Another short duration (5.7 s) hot test on the CE20 engine has been carried out on August 10, 2015 to demonstrate the successful engine ignition with tank pressure conditions as in flight. GSLV Mk III is designed to launch 3.5 to 4 Ton class communication satellites to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit.
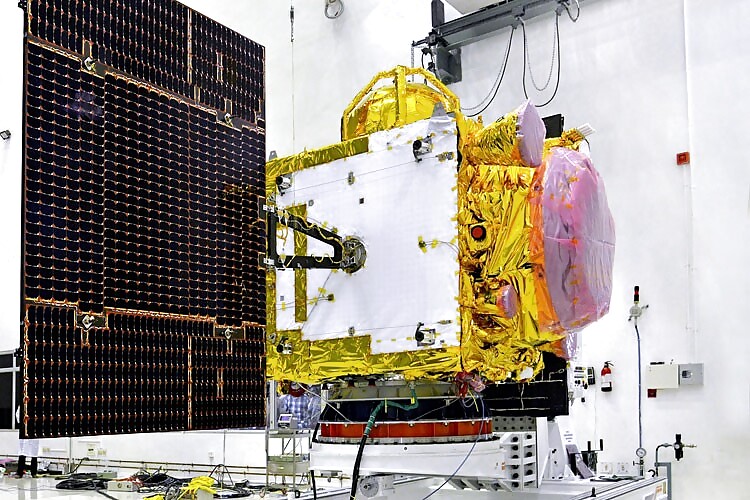

4. Navigational Satellite System:
Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) is designed as a constellation of seven satellites to provide satellite based navigational services in the country. IRNSS-1C, the third Navigational satellite of India, was successfully launched on-board Polar Satellite launch Vehicle PSLV-C26 on October 16, 2014. IRNSS-1D, the fourth satellite in this series was successfully launched on-board PSLV-C27 on March 28, 2015. The first two satellites viz. IRNSS 1A &1B were launched on-board PSLV earlier on July 01, 2013 and April 04, 2014 respectively.
With the operationalisation of four navigational satellites in orbit, it is now possible to provide Position, Navigation and Timing services. The IRNSS constellation of seven satellites is expected to be completed by 2016.
The IRNSS System will benefit the country by providing positioning services over Indian Land Mass and a region extending to the about 1500 Kms around India. The convergence of communication, earth observation and navigation satellite technologies will prove to be a boon in coming years for location based services and informed decision making.
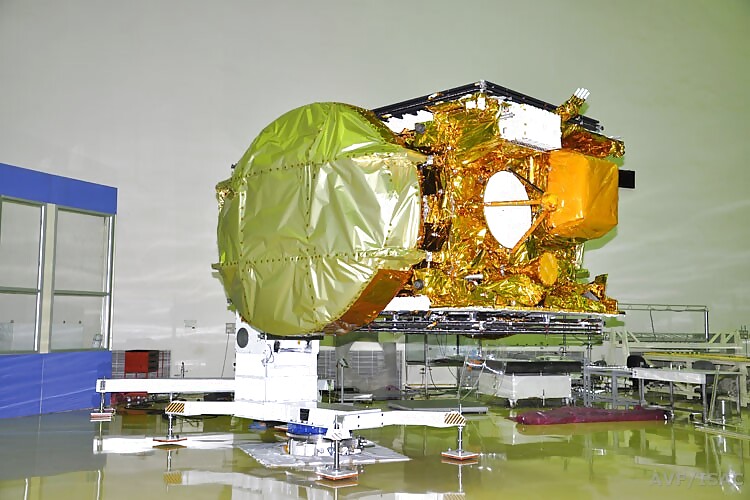

5. Augmenting the Satellite Communications infrastructure:
GSAT-15, a 3 ton class communication satellite (carrying 24 Ku band transponders & GAGAN payload) was successfully launched on November 11, 2015. GSAT-15 will further augment the INSAT/GSAT system capacity for DTH, TV broadcasting, Digital Satellite News Gathering and VSAT services and other societal benefits.
GSAT-6, the country's Advanced Communication Satellite (carrying S-Band payload with 5 spot beams & C-Band Payload with one beam) was successfully launched on August 27, 2015 into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit. The satellite has now been positioned in its designated orbital slot. GSAT-6 is intended to be used for satellite based mobile communications with hand held terminals for strategic applications.
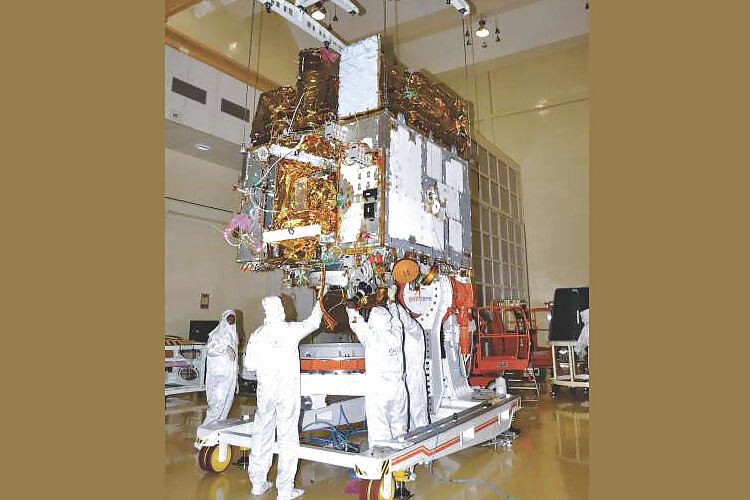

6. India’s first multi-wavelength Observatory in Space:
ASTROSAT satellite, India’s first dedicated astronomy satellite was successfully launched by PSLV-C30 on September 28, 2015. ASTROSAT enables simultaneous Ultraviolet to X-Ray observations to study Stars and Galaxies. It will also provide opportunity to task observations for the scientific community.
ASTROSAT is a unique mission with combination of scientific instruments covering near ultra-violet, far ultra-violet and x-ray bands for multi wavelength observations. The ultra-violet imaging telescope of ASTROSAT has a best resolution of 1.8 arc second combined with large field of view.
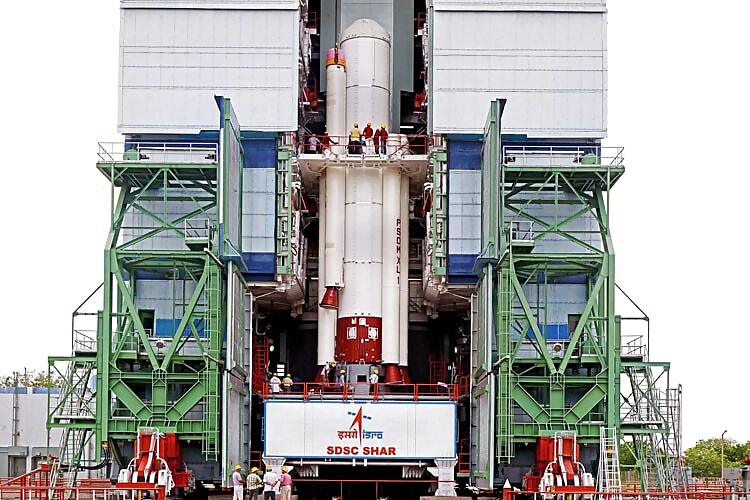

7. Commercial Launch of PSLV:
India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle has launched 17 foreign satellites from seven countries (Canada, Indonesia, Singapore, UK, and USA) during 2015 as given below: (a) India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, PSLV-C28, successfully launched five satellites from United Kingdom and De-orbitsail from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota on July 10, 2015 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota.
PSLV-C30, along with ASTROSAT has successfully launched six co-passenger satellites, 4 LEMUR Satellites (USA), Lapan-A2 (Indonesia) ; NLS-14 (Canada) on September 28, 2015. PSLV-C29 has successfully launched six satellites of Singapore. Of these six satellites, TeLEOS-1 is the primary satellite whereas the other five are co-passenger satellites which include two microsatellites (VELOX-CI, Kent Ridge-1) and three nano satellites (VELOX-II, Athenoxat-1, Galassia)
During the year 2015, a total of 17 foreign satellites were successfully launched from India which takes the total number of foreign satellites launched to 57.
8. National Meet on promoting Space Technology based tools and Applications on Governance & Development:
The one day National Meet on promoting Space Technology based tools and Applications on Governance & Development organized on September 7, 2015 received an overwhelming response with participation of more than 1200 delegates across 60 Central Ministries/Departments, 28 States and 5 Union Territories. The meet comprised of Nine theme sessions (Agriculture, Energy & Environment, Infrastructure Planning, Water Resources, Technology Diffusion, Developmental Planning, Communication & Navigation, Weather & Disaster Management and Health & Education) addressing different domains of national development.
A Special Session was conducted in the presence of the Prime Minister Narendra Modi where he emphasized on the need for new initiatives in all the areas of governance, using the space technology and applications.
9. Initiatives on Satellite for SAARC Region:
ISRO/DOS, with active support from Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), hosted a Conference on “Satellite for the SAARC region and Space Technology Applications” on June 22, 2015 at New Delhi. The conference deliberated on configuration and ground Infrastructure requirements for the proposed ‘Satellite for the SAARC region’ as well as other space technology applications. Representatives from all SAARC member countries have participated.
10. Disaster Management Support:
The Indian Remote Sensing, Meteorological and Communication satellites have immensely helped in the management of recent events of disasters witnessed by the country viz. J&K Floods, HudHud Cyclone and J&K Landslides. These satellites have provided near real time support in terms of early warning, assessment of damages, emergency communication. Flood inundation maps and information on their progression & recession were disseminated on daily basis to concerned agencies.


















Comments
0 comment