
views
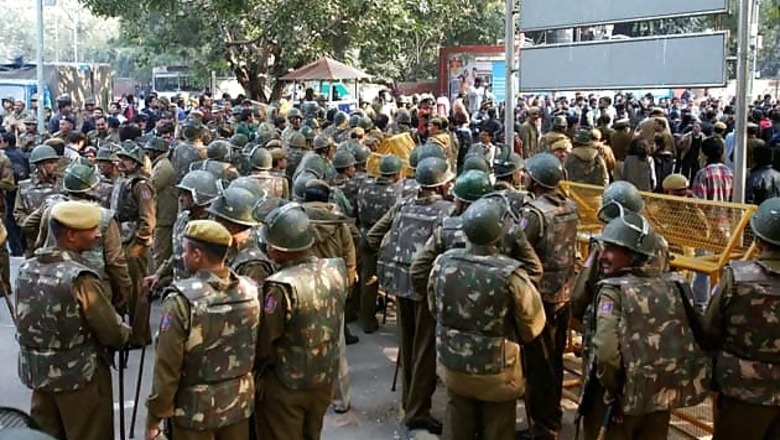
New Delhi: It's no surprise the Indian street wants faster, harsher justice for sexual crimes after a horrific gangrape that rocked the nation, but some activists worry the government will trample fundamental rights in its rush to be in tune with popular rage. The gangrape of a physiotherapy student on a moving bus on December 16 and her death on December 28 in a Singapore hospital triggered a national debate about how to better protect women in India, where official data shows one rape is reported on average every 20 minutes.
Many women's rights groups are cautiously hopeful the protests and outrage that followed the crime can be channelled into real change - fast-track courts for sexual offences and a plan to hire 2,500 new women police in Delhi are measures already in the works. But legal experts and some feminists are worried that calls to make rape punishable with death and other draconian penalties will cramp civil liberties and are unconstitutional. They say India needs better policing and prosecutions, not new laws.
"If there are not enough convictions, it is not because of an insufficiency of law, but it is the insufficiency of material to base the conviction on," said retired Delhi High Court judge RS Sodhi. Five men have been charged with the student's rape and murder. They are due to be tried in a newly formed fast-track court in the next few weeks. A teenager also accused will likely be tried in a juvenile court.
Ahead of Monday's court appearance the five still had no defence lawyers - despite extensive interrogations by the police, who have said they have recorded confessions - after members of the bar association in the south Delhi district where the case is being heard vowed not to represent them.
Grounds for appeal
The men will be assigned lawyers by the court before the trial begins, but their lack of representation so far could give grounds for appeal later should they be found guilty - similar cases have resulted in acquittals years after convictions. "The accused has a right to a lawyer from point of arrest - the investigations are going on, statements being taken, it is totally illegal," said Colin Gonsalves, a senior Supreme Court advocate and director of Delhi's Human Rights Law Network.
Senior leaders of most states on Friday came out in support of a plan to lower to 16 the age that minors can be tried as adults - in response to fury that the maximum penalty the accused youth could face is three years detention. A government panel is considering suggestions to make the death penalty mandatory for rape and introducing forms of chemical castration for the guilty. It is due to make its recommendations by January 23.
"The more you strengthen the powers of the state against the people, the more the possibility you create a draconian regime," said Sehjo Singh, Programme and Policy Director with ActionAid in India and an expert on Indian women's social movements. "We want to raise the bar of human rights in India, we want to raise the standards, not lower them."
Courts are swamped with a backlog of cases in the country of 1.2 billion people and trials often take more than five years to complete, so the launch by Chief Justice Altamas Kabir of six fast-track courts in the capital to deal with sexual offences was widely greeted as a welcome move. Several other states including Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra are now looking at following Delhi's example. But Gonsalves says while the courts are a good idea on paper, similar tribunals in the past delivered dubious verdicts and put financial pressure on the rest of the justice system.
Fast-track courts
India set up 1,700 fast-track courts in 2004, but stopped funding them in 2012 because they turned out to be costly. The courts typically work six days a week and try to reduce adjournments that lead to long delays in cases. "The record of the fast-track courts is mixed," Gonsalves said. Conviction rates rose, he said, but due process was sometimes rushed, leading to convictions being overturned.
"Fast-track courts were in many ways were fast-track injustice," he said. The real problem lie with bad policing and a shortage of judges, Gonsalves said. India has about a fifth of the number of judges per capita that the United States has. Indian police are often poorly trained and underpaid, and have sometimes been implicated in organised crime. Rights groups complain the mostly male officers are insensitive to victims of sexual crimes.
Resources for, and expertise in, forensic science is limited in most of the country's police forces and confessions are often extracted under duress. The judiciary complains it is hard to convict offenders because of faulty evidence. Human Rights Watch said reforms to laws and procedures covering rape and other sexual crimes should focus on protection of witnesses and modernizing support for victims at police stations and hospitals.
The rights organisation has documented the continued use of archaic practices such as the "finger test" used by some doctors on rape victims to allegedly determine if they had regular sex. "Reforms in the rape laws - these are needed. But not in terms of enhancing punishment," said Meenakshi Ganguly, South Asia Director of Human Rights Watch. "Why they are not investigated, why there are not enough convictions, those are the things that need to be addressed."















Comments
0 comment