views
Writing to a Windows Formatted (NTFS) Drive Without Reformatting
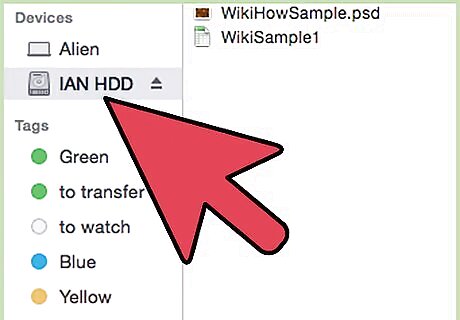
Connect your drive. Using your cable of choice (usually USB), connect your external hard drive to your Mac.
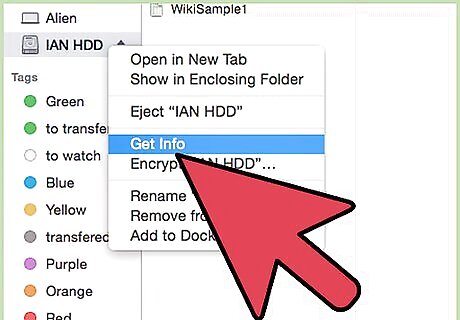
Check the format of the drive. Make sure your external hard drive is NTFS formatted. To do this, right click on your external drive, then click Get Info.
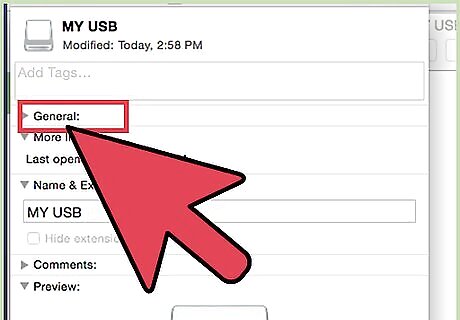
Confirm NTFS formatting. In the Info window, select the General tab. Under this tab should be a Format info field. This should read "Format: NTFS"
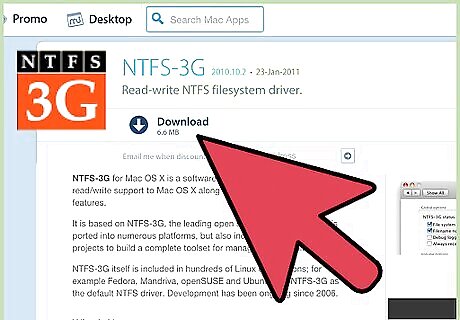
Install third-party software. Mac OS X does not offer native write support for NTFS-formatted drives. In order to write to drives formatted this way, you will need a third-party application or patch. One popular example of this type of software is the open source software NTFS-3G. NTFS-3G's developers also maintain a commercial, more stable, standalone application that enables NTFS writing.
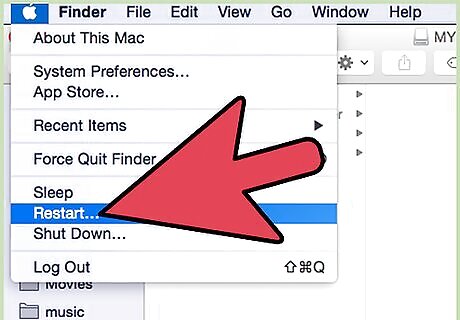
Restart your computer. The installer will ask you to restart your computer. Allow it to restart in order to complete installation.
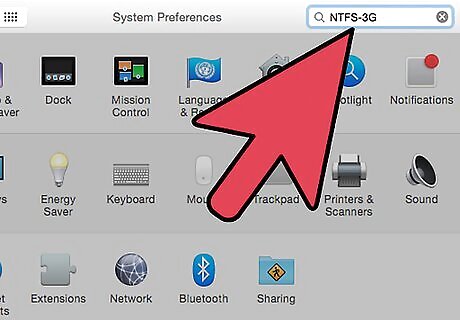
Check for successful installation. After restarting your Mac, you should see a new icon labeled "NTFS-3G" in your System Preferences. This may differ if you are using Tuxera.
Do a test write. Copy a file from your computer to your external hard drive. If it copies correctly, then you may now write files to your external hard drive.
Reformatting a Windows Formatted (NTFS) Drive for Use with OS X
Connect your drive. Using your cable of choice (usually USB), connect your external hard drive to your Mac.
Check the format of the drive. Make sure your external hard drive is NTFS formatted. To do this, right click on your external drive, then click Get Info.
Confirm NTFS formatting. In the Info window, select the General tab. Under this tab should be a Format info field. This should read "Format: NTFS". If the drive is formatted in a way that is write-compatible with OS X, your inability to write may be due to corruption or a faulty cable.
Open Disk Utility. Navigate to your Applications folder, then to Utilities. Locate the application "Disk Utility", and open it.
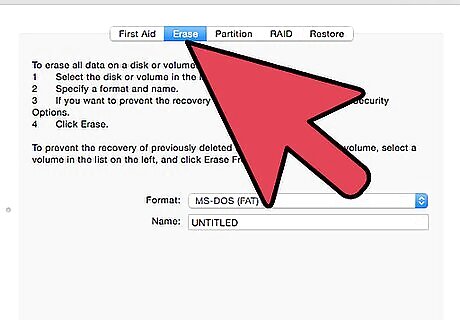
Select "Erase". From the tabbed menus, select Erase. Before proceeding, make sure that all personal data you wish to keep is backed up elsewhere. The reformatting procedure completely erases your data from the drive.
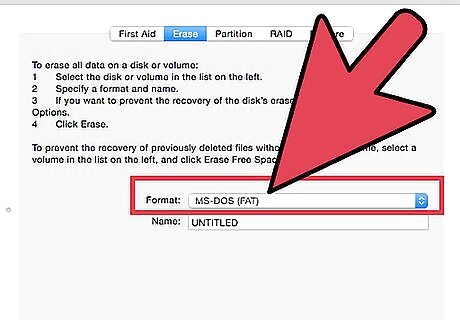
Choose your preferred format. There a few ways that Disk Utility can format your external hard drive. From the dropdown menu labeled "Format", select the format of your choice. You should choose depending on your intentions for your external hard drive. These are the most common formats: FAT: Works natively with both Mac OS X and Windows computers, but is limited to a 4GB maximum file size. exFAT: Works natively with newer versions of Mac OS X (10.6.5+) and Windows (Vista+). Can work with large file sizes. This is the best option for cross-platform compatibility. Mac OS Extended: Works only with Mac OS. Completely incompatible with Windows computers. This is the best option if you intend to use your external hard drive exclusively with computers running Mac OS. NTFS (Windows NT Filesystem): Works natively with Windows, Mac OS write-capability can be added using the steps in the previous Method. This is the best option if you intent to use your external hard drive exclusively with computers running Windows.
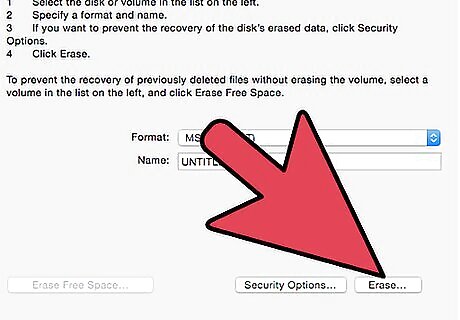
Click "Erase". This will prompt Disk Utility to commence reformatting your drive. The reformatting process should complete within a few minutes.
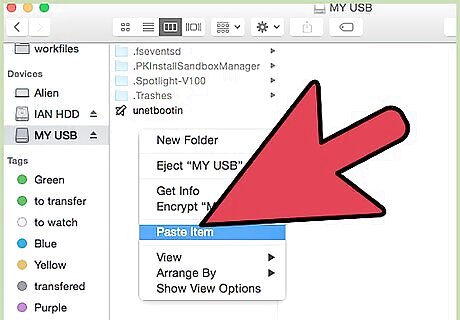
Write to your drive. After reformatting, try copying some files to your external hard drive. Your drive will now be able to accept files written from Mac OS X.
















Comments
0 comment