views
X
Trustworthy Source
MedlinePlus
Collection of medical information sourced from the US National Library of Medicine
Go to source
Ear congestion can result from a cold, allergies, or a sinus infection. It’s also caused by built up pressure from flying, scuba diving, or changing altitudes quickly. Fortunately, you can relieve ear congestion by relieving the pressure in your ears, treating the underlying cause, or removing ear wax. Dealing with ear congestion is never pleasant, but you can get relief by following the right steps.
Getting Quick Relief
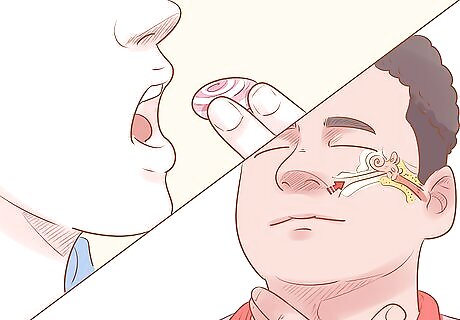
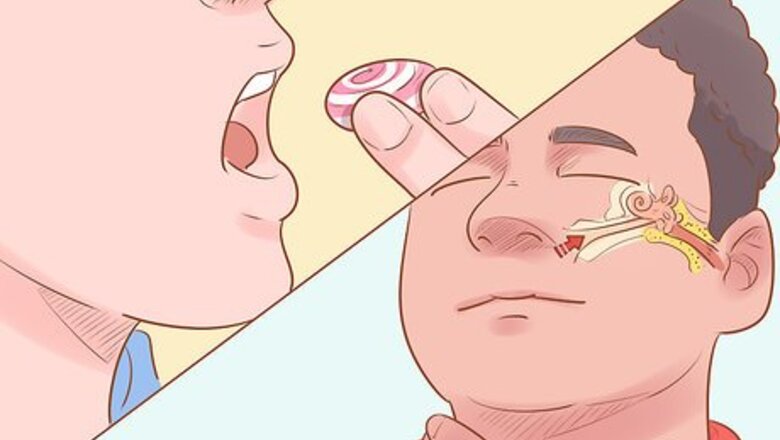
Swallow to open up your eustachian tubes. Swallowing flexes the muscles which control your eustachian tubes, which can cause your tubes to open. You’ll likely hear a popping sound once they open back up. Sucking on a piece of candy can help you make yourself swallow. If you’re flying with a baby, give them a pacifier or bottle to help them swallow.

Yawn. Similar to swallowing, yawning flexes the muscles that control your eustachian tubes. This causes them to “pop” open. Yawning is more effective than swallowing, but some people may find it a little more difficult to induce. If you’re experiencing clogged ears due to airplane ear, yawn during your ascent and descent.
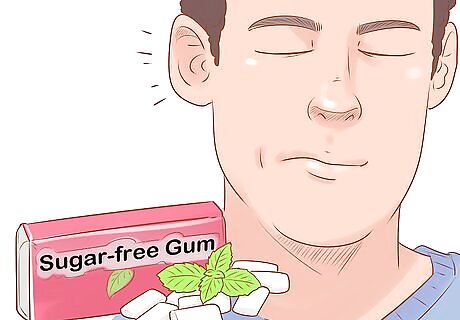
Chew gum. Gum also works your muscles to help open your eustachian tubes. Chew the gum until you hear your ears “pop.”
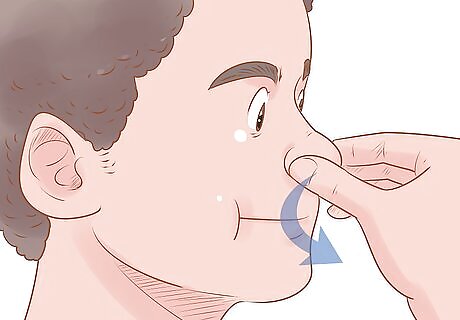
Blow air out through your nose slowly. Take a deep breath. Keeping your mouth closed, pinch your nostrils so that they’re almost closed. Then, slowly exhale through your nose. Listen for a popping sound, which means you’ve been successful. This technique doesn’t work for everyone. After you’ve tried it once or twice and failed, it’s best to try something else. When flying, do this during ascent and descent to avoid congested ears.

Use a neti pot to clear your sinus passages. You can use a neti pot to irrigate your sinus passages, which can relieve your sinus symptoms, including congestion. Fill your neti pot with a sterile solution or distilled water. Tilt your head at a 45 degree angle, then place the tip of the pot against your top nostril. Slowly pour the solution through your nostril, allowing it to come out through the bottom nostril. Blow your nose, then repeat for the other nostril. The neti pot can thin out mucus and flush it away, along with irritants that may be caught in your nasal passages. Carefully follow all of the instructions that come with your individual neti pot so that you do not accidentally inhale the water.

Inhale steam to open up your nasal passages. Pour boiling water into a large bowl, then cover your head with a towel. Lean over so that your face is over the bowl. Slowly breathe through your nose, which will allow the steam to thin out and loosen your mucus. If any mucus accumulates, spit it out. Try putting tea or other herbs into your steam treatment. Some teas, like chamomile, have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic qualities, making them a nice addition to the steam treatment. Hot showers, trips to the sauna, or humidifiers can also help. Avoid placing any steaming object near your ear, as the steam produced this way can sometimes be too hot. Take care not to get too close to the steam, as it can burn your face.
Treating Ear Congestion

Take OTC nasal decongestants if you’ve had a cold, allergies, or a sinus infection. Congested ears often result from sinus congestion, as your eustachian tubes run from the back of your nose to your middle ear. Since nasal decongestants relieve sinus congestion, they can also help unclog your ears. You can find nasal decongestants over-the-counter. For some brands, you may need to ask for them at the pharmacy counter, but you don’t need a prescription. Stop taking the decongestants after 2 days, unless a doctor advises you to continue them. It’s best to talk to your doctor before taking decongestants, especially if you take other medications or have high blood pressure, glaucoma, or prostate problems. Similarly, you shouldn’t give decongestants to children.
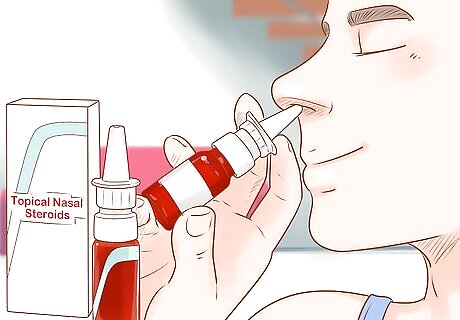
Use topical nasal steroids. Nasal steroids can relieve the swelling inside your nasal passages, which causes congestion. This relieves both your nasal and ear congestion. Don’t use steroids without talking to a doctor. You can find these products over-the-counter or by prescription. These are especially helpful for people who have allergies.

Take an antihistamine if you experience allergies. Untreated allergies can cause ear congestion because they irritate your sinuses, resulting in nasal congestion. A daily antihistamine can help prevent this. There are several options available over-the-counter, including cetirizine (Zyrtec), loratadine (Claritin), and fexofenadine hydrochloride (Allegra). Talk to your doctor before taking an antihistamine or if an OTC antihistamine isn’t working for you. When flying, you can take an antihistamine 1 hour before your flight to help prevent having pressure build up. Read all instructions and precautions enclosed with the medication before taking it.

Visit your doctor for severe or persistent pain. You should start to feel more comfortable within a few hours of starting self-care. If you don’t, then you need to see a doctor. Congested ears can cause damage if left untreated. Additionally, you may have an infection. See your doctor right away if you develop a fever or have any kind of discharge from your ear. Take all of the medication prescribed by your doctor, especially antibiotics. Otherwise, your symptoms may return. Your doctor may be able to prescribe ear drops to help manage pain.
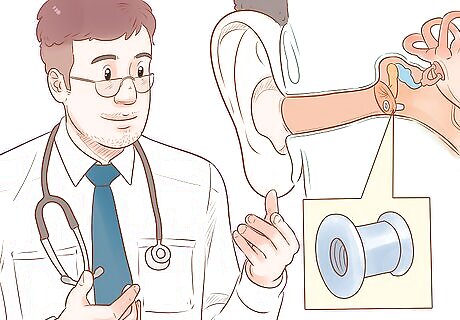
Ask your doctor about ventilation tubes for frequent ear congestion. Your doctor can insert tubes to drain away fluids and relieve the pressure inside the ear. This is most often done when the patient experiences frequent incidences of ear congestion. This is most often done for children who have frequent ear infections. It reduces the incidence of infection and helps the child recover more comfortably.
Clearing Ear Wax Congestion

Tilt your head to the side. The affected ear should be facing up, with your other ear facing the ground. You can make yourself more comfortable by lying down or placing your head against a cushion.
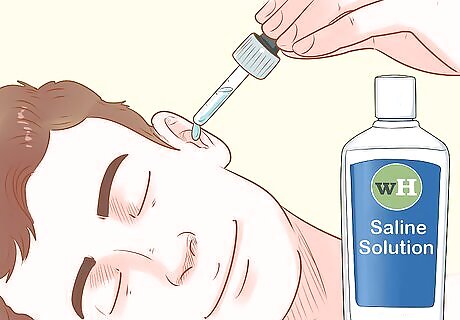
Drip 2-3 drops of water, saline solution, or peroxide into your ear. It’s best to use an eyedropper to avoid adding too much. It doesn’t matter which option you choose, as all will work. However, saline solution and peroxide are sterile, which means they’re less likely to cause an infection if they get stuck in your ear. Do not put any fluid into your ear if you may have an infection or perforated eardrum.
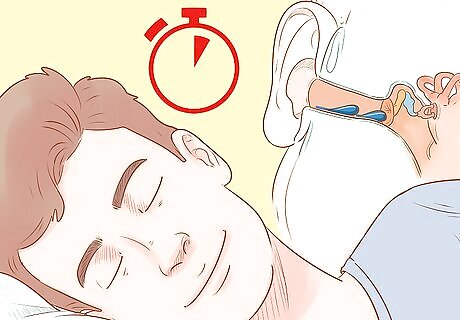
Wait at least a minute for the fluid to drip down into your ear. Gravity will pull the fluid down into your ear, where it will soften the wax. It only takes a minute or so for this to happen. Don’t wait longer than a few minutes, as the liquid could travel further into your ear.

Tilt your head to the other side to allow the wax to drain. The loosened wax should start to drain from your ear with the help of gravity. You may want to place a towel under the ear to catch it. If you’re lying down, simply turn over. As an alternative, you could use a bulb syringe to suck out the loosened wax.
See your doctor if your ear is still congested. The doctor can examine your ear to make sure that it’s just earwax. They can also use a more precise technique to remove the wax, if necessary. If you’ve tried to remove ear wax using items like cotton swabs, then it’s possible that you’ve accidentally made it more compacted. The doctor can help with this.
















Comments
0 comment