views
Learning Language Rules
Look at a pronunciation guide. Pick up a language textbook, or look for a language-learning guide online that focuses on the rules of pronunciation in the language you are interested in. A good pronunciation guide should have a section dealing with silent letters. You could try a language pronunciation guide that uses both text and audio, like How to Pronounce French Correctly by Stanley Connell. You may also be able to find a silent letter pronunciation guide online, like this detailed English example from Kent State University.

Find out which letters are most often silent. Depending on the language you are working with, particular letters may be frequently or always unpronounced. For example: H is always silent in French. In English, if a word follows the CVCV (consonant-vowel-consonant-vowel) pattern, a final E is almost always silent.
Learn the rules of when letters are silent versus spoken. Sometimes, letters that are normally silent in a language are pronounced under special circumstances. For example, many consonants at the ends of words in French are normally silent. However, they may be pronounced when followed by a word that starts with a vowel. E.g.: In “les grands arbres,” pronounce the S in “grands.” In “le gros livre,” do NOT pronounce the S in “gros.” A similar phenomenon can happen in some dialects of English. For example, a final R sound in British English may be pronounced if the next word starts with a vowel. E.g.: In “the baker,” the R in “baker” is silent. In “the baker and I,” the R is pronounced.
Look up the differences in pronunciation in different dialects. Even within a single language, the rules may vary depending on accent or dialect. For example, an R at the end of a word may be pronounced in many dialects of American English, but not in British English. E.g., the word “baker” is pronounced ˈbeɪ.kər (bay-kah) in UK Standard English, and ˈbeɪ.kɚ (bay-ker) in standard American English. In Canadian French, consonants that are usually pronounced in Metropolitan French may be dropped in casual speech. For example, “la” may become just “a”.
Memorizing Common Words and Patterns

Memorize the most common silent letter patterns. Silent letters frequently appear in particular parts of a word (e.g., at the end) or in common combinations with other letters. One good way to know if a letter is silent is to memorize the common patterns or rules in a specific language. For example, in English, GH is usually silent (as in “right,” “eight,” or “neighbor”). So is the K in KN (see “knee,” “know,” “knock”). Look over your pronunciation guide, and take some time to memorize the most common patterns or silent letter combinations.

Learn individual words with silent letters. In addition to memorizing common pronunciation patterns, you may need to memorize individual words with silent letters. This is especially important in hybrid languages like English, where some words do not follow the common pronunciation “rules.” For example, while an H at the beginning of an English word is usually pronounced, it is silent in words like “hour,” “honor,” and “herb.” Write out a list of common words that contain silent letters. You may also be able to find a list of these words online or in a language textbook.

Make flashcards. Flashcards are a great aid for memorizing vocabulary and pronunciations. Put together flashcards from your list of words with silent letters. Quiz yourself with flashcards, or practice using them with a friend or study partner. For word flashcards, you could write the word on one side, and spell it out phonetically on the other side (e.g., “Chartreux” on the front, “shartru” on the back).
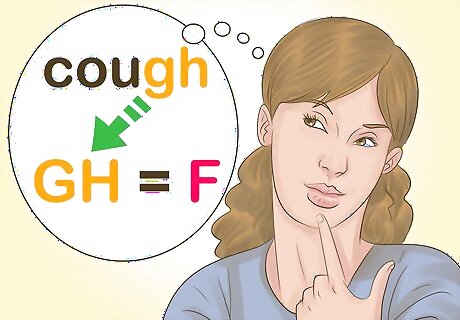
Keep an eye out for exceptions. Even if you know the “rules” for recognizing silent letters in a particular language, there will always be exceptions. Check a language book or pronunciation guide for words that are commonly mispronounced because they do not follow the expected pattern for silent letter use. For example, in English, the words “cough” and “tough” break the usual pattern of a silent GH. In these words, GH is pronounced with an “F” sound as opposed to being silent, as in “right” or “weigh.”
Looking up Word Pronunciations

Check a dictionary entry for a phonetic spelling. If you’re really unsure of whether a letter is pronounced or silent in a particular word, you can find out by looking up the pronunciation of that word in a dictionary. However, note that many dictionaries use the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to show how a word is pronounced. If you do not know how to read IPA, check your dictionary for a pronunciation key.

Look up the word’s pronunciation online. Many online dictionaries or language guides provide audio clips, so you can hear how a word is pronounced. For example, the online Cambridge Dictionary of English provides audible pronunciations of words as well as IPA spellings. You can also find audible pronunciation guides on sites like Wiktionary or YouTube.

Ask a fluent speaker of the language how to pronounce the word. If you know someone who is familiar with the language and the word in question, you can ask them how to pronounce it. Try to ask someone who is fluent in the language that the word belongs to. You might ask someone who speaks it as their first language, or who teaches the language. If a word is particularly technical or obscure, the average speaker of the language may not be familiar with it. For example, many English speakers may not know that the CH is silent in “chthonic.”



















Comments
0 comment