
views
Eat more dark chocolate.

The flavanols in cocoa may boost blood flow to your brain. A recent study showed that when participants drank a cocoa beverage that was formulated to be rich in flavanols, they showed increased regional blood flow in the brain. While you might not find that same concentration of flavanols in your favorite candy bar, there can be up to 2000 mg of flavanols in a 3 oz (90 g) piece of dark chocolate. You can also find flavanols in natural (not Dutch-processed) cocoa powder. Of course, you should still enjoy chocolate in moderation, and avoid add-ins like marshmallows or caramel that are high in sugar and fat. A good rule of thumb is that you can have about 1 oz (30 g) of dark chocolate a few times a week.
Chew gum.

It might sound far-fetched, but there's science behind this. Studies have shown that when a person chews gum, they have increased regional cerebral blood flow to widespread areas of their brains. Research is still being done on how effective this is and what impacts it might have, but if you need to feel a little sharper, popping a stick of chewing gum might be a good idea!
Drink beet juice.

Beet juice may help widen your blood vessels. Beets contain nitrates, which are then converted to nitrites in your body. Nitrates help increase the size of your blood vessels, which allows them to carry more blood to key areas of your body—including your brain. Beets contain particularly high levels of nitrates, but nitrates are also found in leafy green vegetables like spinach, cabbage, and lettuce, along with fennel, celery, radishes, and parsley. You can still get nitrates from eating these vegetables, so it's fine if you prefer eating beets to drinking beet juice. Drinking the juice just allows you to ingest the nitrates more quickly.
Enjoy plenty of berries.
The antioxidants in berries can stimulate blood flow to your brain. Specifically, eating berries seems to increase blood flow to the areas of your brain used for memory and paying attention to tasks. Furthermore, they help protect your brain from oxidative stress, which can deteriorate your brain function over time. Try eating 1 cup (150-200g) of berries each day to get brain-boosting benefits. It doesn't matter if the berries are fresh, dried, or frozen. Strawberries, blueberries, blackberries, mulberries, bilberries, and black currants have all shown promising results in studies.
Listen to your favorite music.

Turning on the tunes you love the most can fire up your brain. Studies show that when people listen to their favorite songs, they have increased blood flow to their brains. It doesn't really matter what type of music it is—as long as it's something you enjoy listening to. Try listening to a song you love right before you do a task you really need to focus on and see if it helps! Learning a new language can also help increase blood flow to your brain by encouraging you to think more. Blood flow to your brain also increases when you're reading—although interestingly, different areas of your brain are activated when you're studying than when you're reading for pleasure.
Get a good night's sleep.

Your brain gets more blood while you're sleeping. It might seem simple, but just getting enough sleep can help improve your brain health. It's thought that the increased blood flow helps clean out any metabolic waste that accumulated in your brain during the day. That's a big part of the reason why you feel foggy when you stay up too late. If you're 13-18 years old, you need 8-10 hours of sleep each night. If you're 18-60, you need at least 7 hours of sleep every night.
Exercise 3-4 times a week.
Any moderate activity will have positive effects on your circulation. You don't necessarily have to engage in strenuous or lengthy sessions to get a benefit—the important thing is that you get up and moving. Even taking a short walk or spending some time on a stationary bike can help improve the blood circulation to your brain. Find an activity you really like doing, such as swimming, bicycling, dancing, playing a sport, or walking in the park. The more you enjoy it, the more likely you'll be to stick to it! Use a timer throughout your day to remind yourself to take walking breaks.
Stretch throughout the day.
Stretching will improve your overall circulation. This will increase the blood flow to your muscles, thereby improving and increasing the circulation to your brain. Try setting aside a few minutes every hour to stretch your body—you might just notice that you feel a little sharper afterward. Simple stretches that result in increased blood flow to the brain include touching your knees or toes from a standing position. Alternatively, sit with your legs outstretched and touch your knees, shins, or toes. When you're stretching, be careful not to do anything that causes pain or discomfort in your back. Some people believe that inversion poses in yoga will increase blood flow to the brain, but this has not been scientifically proven.
Practice meditation.
Blood flow increases in several parts of your brain when you meditate. That's right, meditating can do more than just leave you feeling centered and focused. There are also physical brain-based benefits to getting in touch with your inner self has physical benefits. One of the areas stimulated during meditation is your prefrontal cortex. This part of your brain has a big role in controlling your attention span, impulse control, and memory formation. You may also benefit from the slowed breathing that usually occurs during meditation, as this increases the saturation of oxygen in your blood. There are many ways to meditate. An easy way to begin a meditation practice is simply to sit comfortably with your eyes closed, and count your breaths. When you have counted 10 breaths, start over. Focus your entire attention on counting your breaths—when other thoughts enter, simply notice them and let them go.
Loosen your necktie.
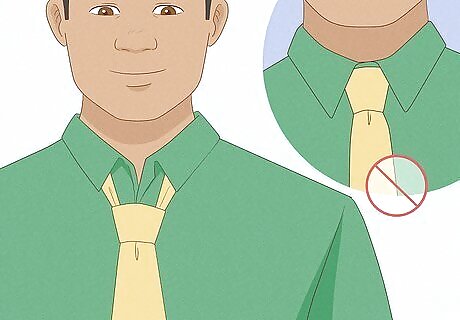
Wearing a tight necktie can decrease circulation to your brain. You might not notice a dramatic difference if your tie is too tight—your brain will still have healthy levels of blood and oxygen. However, if you already have other risk factors that are causing decreased blood flow, this might be a simple way to help improve your brain's circulation.
Get GV20 acupuncture.
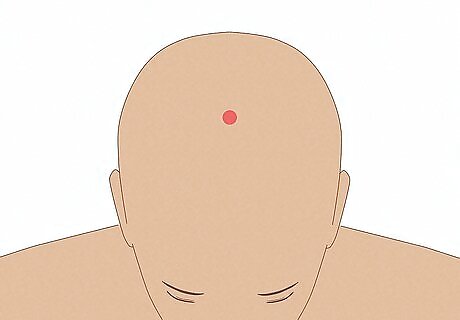
GV20, or Baihui, is located at the very top of the head. If you're trying to increase the blood flow to your brain, ask an acupuncturist to stimulate your GV20 acupoint. One study showed a significant increase in blood flow to certain areas of the brain after a GV20 acupuncture session. There wasn't any increase in the subjects' arterial blood pressure or pulse, however. This isn't something you should try on your own—find a licensed acupuncture practitioner who's experienced with this acupoint.
Undergo light therapy.

Light therapy is often used for seasonal affective disorder. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and other depressive disorders have been linked to a decrease in brain blood flow. In one study, patients who were responsive to light therapy were found to have increased blood flow to their brains after the treatment. You can buy light therapy boxes online. However, it's a good idea to talk to your physician or mental health care provider before you start light therapy on your own, especially if you have SAD combined with bipolar disorder or certain eye problems like glaucoma, cataracts, or diabetic eye damage.
Avoid cigarettes.
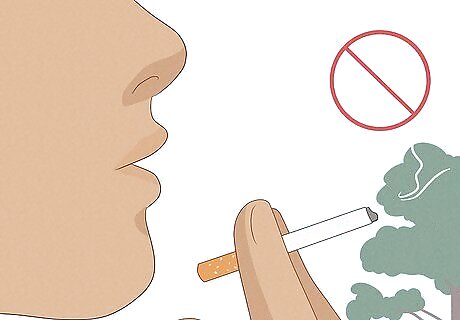
Take steps to quit if you're a smoker. Nicotine restricts arteries, which prevents healthy blood flow to the brain. On the other hand, the brain's oxygen uptake and blood flow decrease by up to 17% immediately after people stop smoking. Smoking has been linked to strokes and brain aneurysms. An aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel caused by a weakness in the blood vessel wall. E-Cigarettes contain nicotine, which constricts blood vessels and lowers the blood flow to the brain. They are not recommended as a substitute for ordinary cigarettes. If you're having trouble quitting, talk to your doctor about smoking cessation aids that may help.



















Comments
0 comment