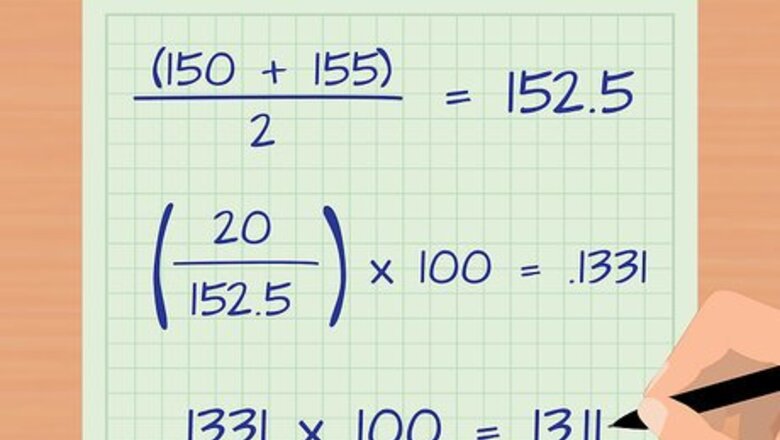
views
Calculating Attrition Rate
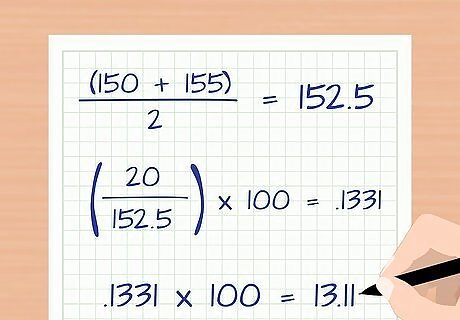
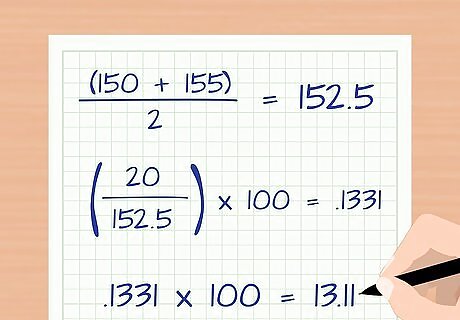
Calculate the monthly attrition rate. To calculate the attrition rate for any given month, you need to know the total number of employees at the beginning of the month. Then, you need to know the number of new employees added that month. Finally, determine the number of employees who left. The number of employees who left is the number of attritions. Plug the numbers into the following formula: Attrition Rate = Number of Attritions/Average Number of Employees *100. For example, suppose a telecommunications company had 150 employees as of April 1, 2015. During that month, 20 employees voluntarily left the company. Also, the company hired 25 new employees. First, calculate the average number of employees. The beginning number was 150. If 20 people left and 25 people were hired, then the ending number was 155. The average number of employees for that month can be calculated with the equation ( 150 + 155 ) / 2 = 152.5 {\displaystyle (150+155)/2=152.5} (150+155)/2=152.5. Next calculate the monthly attrition rate. In this month, 20 people left, and the average number of employees was 152.5. The monthly attrition rate can be calculated with the equation ( 20 / 152.5 ) ∗ 100 = .1311 ∗ 100 = 13.11 {\displaystyle (20/152.5)*100=.1311*100=13.11} (20/152.5)*100=.1311*100=13.11 The attrition rate for April, 2015 was 13.11 percent.

Calculate the quarterly attrition rate. Use the same formula. However, instead of one month of data, you will look at the data for one quarter, which is three months. Suppose the telecommunications company in the above example wants to calculate its attrition rate for the second quarter of the 2015. This would be April, May and June 2015. The beginning number of employees on April 1, 2015 was 150. Over the course of the quarter, 30 people left and 40 new employees were hired. Therefore, the ending number of employees on June 30, 2015 was 150 − 30 + 40 = 160. {\displaystyle 150-30+40=160.} 150-30+40=160. The average number of employees for the quarter was ( 150 + 160 ) / 2 = 155 {\displaystyle (150+160)/2=155} (150+160)/2=155. The attrition for the second quarter of 2015 was ( 30 / 155 ) ∗ 100 = 19.35 {\displaystyle (30/155)*100=19.35} (30/155)*100=19.35, or 19.35 percent.

Calculate the annual attrition rate. For this calculation, you need to know the total number of attritions for the year. Then, you need to calculate the weighted average of employees. Using the weighted average is more mathematically accurate since it smooths the effect of seasonal changes in the number of employees a company has throughout the year. Suppose the telecommunications company in the above example had a total of 62 attrition for the year. They typically hire 20 percent more employees for the last quarter of the year for their busy season. So, they have an average of 155 employees for the first three quarters, and an average of 186 employees for the last quarter. Knowing that there are four quarters in a year, you could calculate the weighted average with the formula ( ( 155 ∗ .75 ) + ( 186 ∗ .25 ) ) = ( 116.25 + 46.5 ) = 162.75 {\displaystyle ((155*.75)+(186*.25))=(116.25+46.5)=162.75} ((155*.75)+(186*.25))=(116.25+46.5)=162.75. You could also use the number of weeks worked. There are 52 weeks in a year. In the first three quarters, there are 39 weeks, and in the last quarter there are 13 weeks. Use the formula ( ( 155 ∗ 39 ) / 52 ) ) + ( ( 186 ∗ 13 ) / 52 ) ) = 116.25 + 46.5 = 162.75 {\displaystyle ((155*39)/52))+((186*13)/52))=116.25+46.5=162.75} ((155*39)/52))+((186*13)/52))=116.25+46.5=162.75. Finally, you could use the number of hours worked. In a year, there are 2080 work hours. In the first three quarters, there are 1,560 hours, and in the last quarter there are 520 hours. Use the formula ( ( 155 ∗ 1 , 560 ) / 2080 ) ) + ( ( 186 ∗ 520 ) / 2080 ) ) = 116.25 + 46.5 = 162.75 {\displaystyle ((155*1,560)/2080))+((186*520)/2080))=116.25+46.5=162.75} ((155*1,560)/2080))+((186*520)/2080))=116.25+46.5=162.75 The weighted average of employees for this company is 162.75. Calculate the annual attrition rate with the formula ( 62 / 162.75 ) ∗ 100 = 38.09 {\displaystyle (62/162.75)*100=38.09} (62/162.75)*100=38.09, or 38.09 percent.
Projecting the Attrition Rate

Understand the value of projecting the attrition rate. While it’s valuable to look at the historical attrition rate, businesses need to be able to project the attrition rate to gauge the company’s future performance. The projected attrition rate can be compared to attrition rates in other businesses in the same industry or sector. If an unfavorable attrition rate is projected, businesses can implement strategies now to reduce employee turnover.
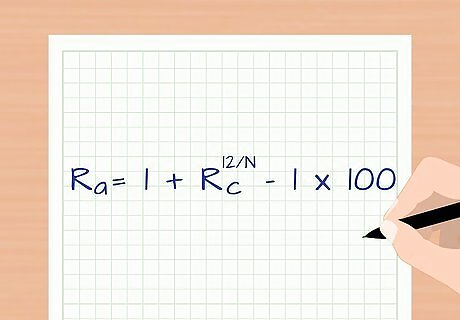
Learn the formula for annualizing data. If you know the number of attritions for a few months, you can extrapolate this information for the rest of the year. Remember that this number is a projection. It may not take into account seasonal changes that may impact the true attrition rate. Use the formula R a = 1 + R c 12 / N − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1+R_{c}^{12/N}-1*100} R_{a}=1+R_{c}^{{12/N}}-1*100. R a {\displaystyle R_{a}} R_{a} = annualized attrition rate R c {\displaystyle R_{c}} R_{c} = cumulative attrition rate N {\displaystyle N} N = the number of time periods observed.
Annualize the attrition rate from monthly data. Suppose a company wants to use data from January to May to annualize its attrition rate. On January 1st, the company had 2,050 employees. The number of attrition was 125, and the number of new hires was 122. Therefore, the ending number of employees was 2,047. Calculate the cumulative attrition rate to date. The average number of employees was 2,048.5 ( ( 2 , 050 + 2 , 047 ) / 2 = 2 , 048.5 {\displaystyle (2,050+2,047)/2=2,048.5} (2,050+2,047)/2=2,048.5). The cumulative attrition rate was 6.1 percent ( ( 125 / 2 , 047 ) ∗ 100 = 6.10 {\displaystyle (125/2,047)*100=6.10} (125/2,047)*100=6.10). Annualize the attrition rate. The cumulative attrition rate is 6.1 percent and the number of time periods observed is 5 (January through May is five months). R a = 1 + .061 12 / 5 − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1+.061^{12/5}-1*100} R_{a}=1+.061^{{12/5}}-1*100 R a = 1.061 2.4 − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1.061^{2.4}-1*100} R_{a}=1.061^{{2.4}}-1*100 R a = 1.153 − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1.153-1*100} R_{a}=1.153-1*100 R a = .153 ∗ 100 = 15.3 {\displaystyle R_{a}=.153*100=15.3} R_{a}=.153*100=15.3 The annualized rate of return is 15.3 percent.
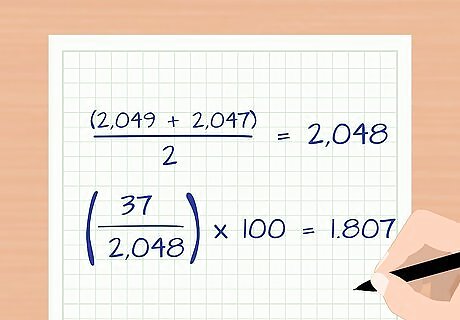
Project the quarterly attrition rate. Use the same formula, only instead of 12 months, use 3 months. For example, suppose the same company in the example above wanted to use its April and May data to project attrition for the entire second quarter. On April 1st, the company had 2,049 employees. The number of attritions in April and May was 37, and the number of new hires was 35. Therefore, the ending number of employees as of May 31st was 2,047. Calculate the cumulative attrition rate for the quarter. The average number of employees was 2,048 ( ( 2 , 049 + 2 , 047 ) / 2 = 2 , 048 {\displaystyle (2,049+2,047)/2=2,048} (2,049+2,047)/2=2,048). The cumulative attrition rate for those two months was 1.81 percent ( ( 37 / 2 , 048 ) ∗ 100 = 1.807 {\displaystyle (37/2,048)*100=1.807} (37/2,048)*100=1.807) Extrapolate the attrition rate for the rest of the quarter. The cumulative attrition rate is 1.81 percent and the number of time periods observed is 2 (April and May). R a = 1 + .0181 3 / 2 − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1+.0181^{3/2}-1*100} R_{a}=1+.0181^{{3/2}}-1*100 R a = 1.0181 1 .5 − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1.0181^{1}.5-1*100} R_{a}=1.0181^{1}.5-1*100 R a = 1.02727 − 1 ∗ 100 {\displaystyle R_{a}=1.02727-1*100} R_{a}=1.02727-1*100 R a = .02727 ∗ 100 = 2.727 {\displaystyle R_{a}=.02727*100=2.727} R_{a}=.02727*100=2.727 The projected attrition rate for the second quarter is 2.73 percent.
Analyzing the Impact of Attrition Rate

High attrition rates can damage a company’s brand. Customers rate their satisfaction with a company largely on their relationship with its employees. Customers may think they are purchasing inferior products or receiving diminished services because of the change in personnel. They may attribute this to lower staffing levels or lack of morale and motivation on the part of the remaining employees.
Attrition rates impact the bottom line. If businesses lose customers due to high attrition rates, this naturally impacts the bottom line. One abstract study concluded that high attrition rates impacted one company’s profitability by as much as 400 percent. They looked at different branches of a temporary help services firm. The branches with the highest attrition rates tended to be about four times less profitable than those with the lowest attrition rates. Demystify key business metrics. "As a new manager, I felt totally clueless trying to make sense of stuff like "attrition rates" in all those financial reports. But this article explained everything in simple terms, even showing step-by-step how to actually calculate those numbers. Now, turnover and retention finally make sense to me. I can track what's going on and explain it to others." - Tina S. Enhance budget accuracy. "With lots of employees quitting, our budgets for hiring new people were always way off. The tips here on forecasting turnover helped me figure out how many employees we realistically need to plan and pay for. Our CFO is stoked that we've got way more accurate numbers to work with now." - Mohamm F. Spot issues causing a turnover. "We knew turnover was high from all the exit interviews, but I couldn't pinpoint exactly where the problems were. By comparing our stats to industry standards, I saw we were losing way too many new hires. That let me majorly revamp our training program. Now we keep those employees longer." - Rajkumar J. Safeguard customer loyalty. "Relying on short-term contractors hurt quality control a ton. Using the metrics here showed me constant churn was probably making customers unhappy, too. So we've committed to keeping staff longer through better benefits. Rebuilding those loyal customer bonds will be crucial for sales." - Rose A. Have a story our readers should hear? Share it with 1 billion+ annual wikiHow users. Tell us your story here.

Improving employee retention rates can save businesses money. When an employee leaves, a company may spend as much as one-fifth of that employee’s salary to replace that employee. If a business experiences a high rate of attrition, this can represent a significant cost. Productivity losses when someone leaves, the cost of hiring and training a new employee and slower productivity until the new worker learns the job contribute to these costs. Companies can avoid these expenses by implementing policies that improve employee retention. Workplace flexibility, accrued sick time and paid family leave may help reduce loss of employees. EXPERT TIP Paridhi Jain Paridhi Jain Certified Public Accountant Paridhi Jain is a Certified Public Accountant and the Co-Founder of Seva Ltd, a CPA firm operating in Maryland and Alabama. She has over 10 years of professional experience in the financial sector and has built a reputation for assisting small business owners navigate the intricacies of regulatory compliance, encompassing areas from company structuring and entity formation to detailed nexus determinations for income and sales tax. She is an active member of the Alabama Society of CPAs and has a certification in pre-professional accounting. She graduated Magna Cum Laude from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County with a major in Information Systems. Paridhi Jain Paridhi Jain Certified Public Accountant Attrition rate calculations help companies budget for staff turnover. The attrition rate is the percentage of employees that leave a company over a period of time. Say a company hired 10 people in January, but historically 40% leave each year. They'd expect 4 of those 10 to quit before next January. Businesses need to know likely turnover numbers to budget for staffing properly.

















Comments
0 comment