views
Adding the Fish
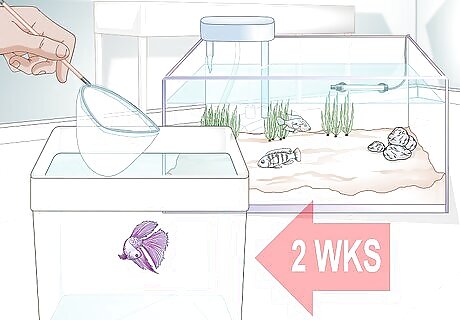
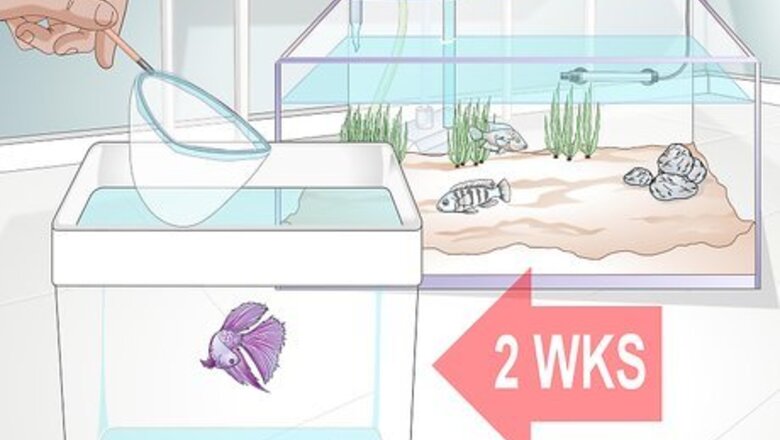
Quarantine the betta. Before you add the betta to a community, it needs to be quarantined. This will give you time to monitor the betta’s condition to ensure it does not develop illnesses that it could then spread to the rest of the fish in the community tank. During the two-week quarantine period, ensure that your fish eats properly, demonstrates normal activity, and remains free of signs of parasites. If your fish does show signs of illness during the quarantine period, take it to a vet. Common symptoms of illness in betta fish include a bloated body or a refusal to eat (constipation), fluffy white growths on its body (fungus), torn or disintegrating fins (fin rot), small white spots on the body or fins (ich), or a grayish slime covering the body or fins (slime disease). Any other behavioral abnormalities or symptoms of illness should be taken seriously and referred to a veterinarian. Obtain betta fish from qualified betta breeders. A breeder is more likely to give you a healthy fish than a pet store.
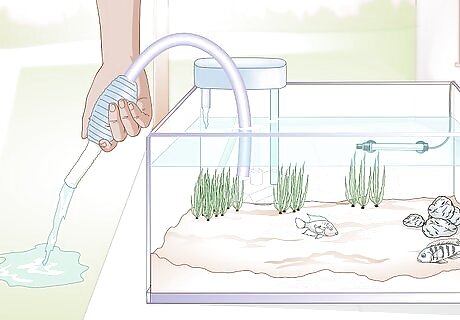
Ensure your tank is clean. Use visual checks to ensure your tank is free of algae and debris floating on top of the water or settled on the bottom. Ensure your tank’s filter is clean and operating properly. Add a UV sterilizer to reduce the risk of disease. If necessary, change your tank’s water. When cleaning the gravel, avoid taking it out and rinsing it in hot water, as this will kill any beneficial bacteria that's been established and is necessary to maintain proper water quality. Instead, use a gravel siphon as part of your regular water change maintenance schedule.
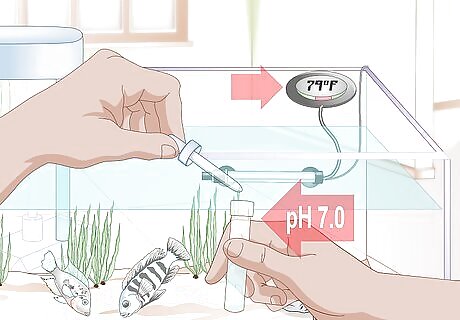
Check environmental conditions. The tank’s conditions should be within the parameters a betta fish can tolerate. Check the thermometer to ensure the temperature is between 78 and 82 degrees Fahrenheit (about 26 degrees Celsius). Use your pH meter to make sure the acidity is between 6.5 and 7.5. The ammonia should stay at 0, nitrates at 5-20 ppm, and 0 nitrite. To ensure a proper temperature, use a good thermometer that's easy to read. You can also use a betta-safe adjustable heater and adjust the temperature accordingly. If your tank is too cold, invest in a heat lamp, in-tank heater, or under-tank heater. These are readily available at most pet stores. Get a small pH test kit from your local pet store or online to check the pH level. If you want to lower the pH level in the tank, you’ll need to add an acidic compound specially designed for fish. Indian almond leaf (IAL) and blackwater extract (BWE) are common additives. You could also add peat to your filter and add some untreated wood to your tank. If you want to increase the pH, add a crushed coral or limestone chip substrate. Check your local pet store for materials and compounds to adjust pH levels. Always follow specific use directions when adjusting pH levels. Dramatic changes could negatively impact your fish.
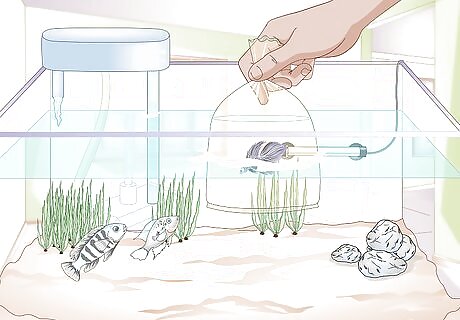
Acclimate your betta to the community. After the quarantine period is over, your betta is ready to join the other fish. Turn off the aquarium lights and dim the aquarium room’s overhead lights. Transfer the betta to a small plastic bag. Float the bag (with the betta fish still in it) in the water of the community tank for about 15 minutes. Move it slowly and gently through the water. This helps the water temperature in the bag approach the water temperature in the tank.
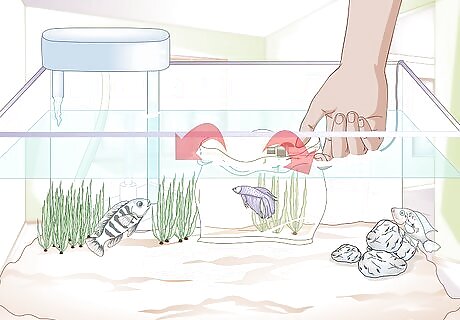
Fold the top edges of the bag down. The edges of the bag should be rolled down so that they are slightly submerged in the water. The air trapped between the rolled-down edges and the bag should allow the bag (and the betta fish within) to continue floating without your help.
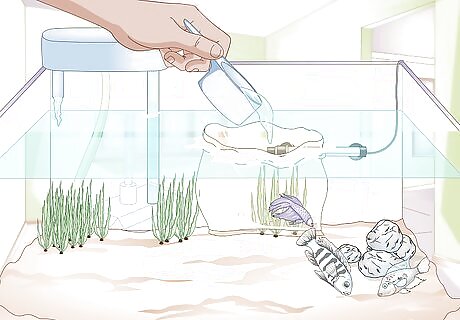
Add water to the bag. Every four minutes, add about half a cup of tank water to the bag. When the bag is full, dump out half the water from the bag, then float it in the tank again. Begin filling the bag with tank water again, adding half a cup every four minutes. When you fill it to the top for a second time, net the betta fish and place it in the tank. Dump out the water you placed in the bag.

Monitor your fish. Keep a close eye on your betta for the first few days after adding it to the community tank. Look for signs that the community arrangement is not working out, such as conflicts between the betta and other fish, or finding your betta fish floating alone in a corner of the tank. Have a backup plan before adding the betta to the community tank. If the betta is not accepted by the community, the best backup plan you can enact is to simply transfer the betta back to an individual tank of at least five gallons. Major warning signs include missing scales, visible bits missing from the betta’s fins (due to being bitten), disappearance of community fish (due to the betta eating them), or the presence of stress stripes (darkly colored horizontal stripes along the betta’s body). Do not confuse stress stripes with a female’s breeding stripes, which are vertical.
Choosing the Fish to Add
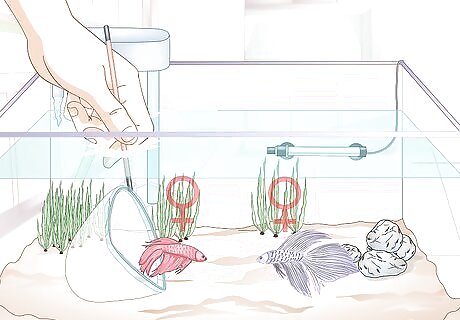
Choose the sex of your fish. While you can add a female betta to a community with other female betta fish, it is not recommended that you keep male betta fish in the same tank as other males. Males can be extremely aggressive and territorial, especially when they see other betta fish. Females are generally less aggressive and territorial than males, but you should keep an eye on any betta fish in your tank -- male or female -- for problematic behavior. Do not attempt to mix male and female betta fish unless you’re trying to breed them. If this is the case, monitor their interactions carefully and separate them at the first sign of conflict.
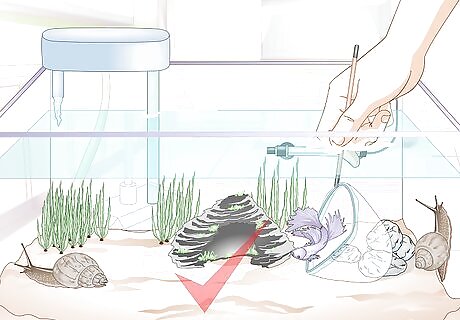
Add a curious fish. A community tank offers more opportunity for exploration and enrichment than a solitary tank. Even though betta fish prefer having their own space, they are quite intelligent. A community tank with non-threatening fish, snails, and other creatures will keep the betta engaged and active. If you have not already decked your community tank out with fake plants, little fish houses, tubes, rocks, and hidey holes, consider adding some. Betta fish (and other species) enjoy exploring these spaces. Make sure that there are plenty of plants in these hiding spots.
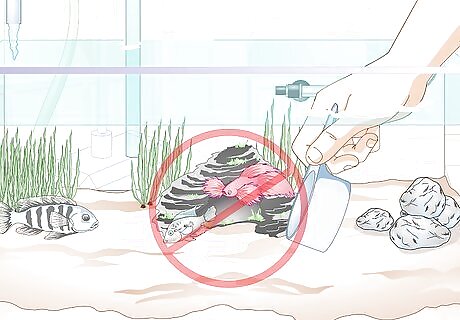
Do not add aggressive fish to a community tank. While male betta fish, especially, tend to be very aggressive, all betta fish are solitary by nature and can be aggressive if they perceive that another fish is in their zone. Often, the only way to know if your betta would fit into a community tank is to try it. However, if you’ve had your betta in contact with another community before, use that experience as a guide when thinking about whether or not the fish would like to live in another community. Look for fast-moving, non-aggressive tank mates, such as small tetras (like cardinals or neons). Avoid fish like tiger barbs and larger tetras, as they can be too aggressive to the betta. Ultimately, the betta should be the centerpiece of the aquarium, and every other fish should be compatible with it.
Matching a Betta to an Appropriate Community

Determine compatible species. Certain fish are more appropriate as betta tankmates than others. Cories, for instance, are bottom feeders and share space easily with betta (who prefer swimming along the top of the tank). Loaches and otocinclus catfish, likewise, are also bottom feeders and therefore compatible with betta fish. Other species that you could select for a betta community include: Ghost shrimp -- these shrimp are entirely transparent, making it difficult for betta fish to see them. Other sorts of shrimp such as Red Cherry shrimp may be eaten by the betta fish. Snails -- any sort are good for a betta community, since they do their own thing along the bottom of the tank. Feeder guppies -- these guppies are dull in color and thus unlikely to attract the betta’s attention. Most corydoras, kuhli loaches, rasboras, white cloud mountain minnows, tetras, and bristlenose plecos also make good tankmates.
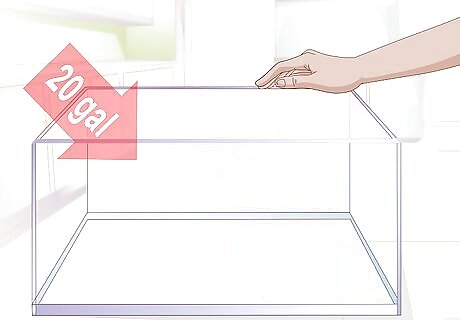
Select the right sized tank. The minimum tank size for any community tank is 20 gallons. Bettas generally like to move around their tank to explore. It is therefore important to provide a tank of the appropriate size. Bettas should get at least 2.5 gallons (9.5 L) for themselves. Think about the spatial needs of the other fish and creatures in the community before introducing a betta. Ensure the community tank is not overcrowded.
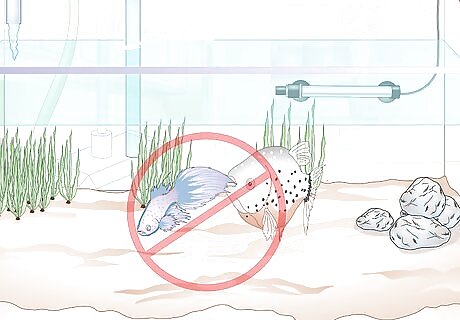
Do not add betta fish to a tank with fin nippers. Despite the betta's aggressive reputation, their long fins can be attractive to fin-nipping fish, which can create a lot of stress for the betta. Tiger barbs, for instance, should not be in the same tank as a betta. This is not a mere annoyance for the betta fish. Nipped fins can become infected and lead to increased stress.
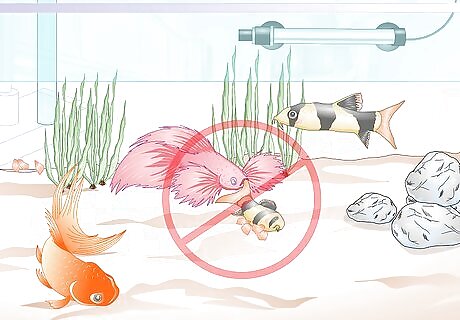
Do not add a betta fish to a tank with colorful fish. Betta fish will perceive most guppies, goldfish, tropical fish, and other bright and multicolored fish as enemies or rivals. Only in rare instances (such as when a betta is housed with another especially shy betta) can it live in peace with colorful fish or guppies.
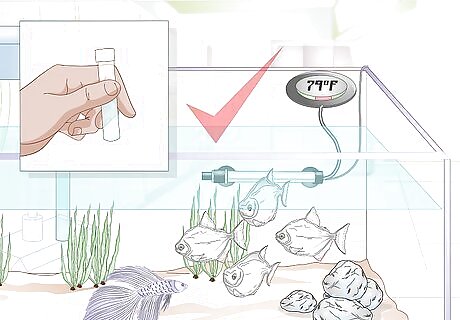
Add fish that share the same environmental conditions as the betta. Betta fish prefer water with a pH of between 6.5 and 7.5. The temperature of a tank with betta fish in it should simulate the temperature of the tropics, around 78 to 82 degrees Fahrenheit (about 26 degrees Celsius). Finally, the community tank you’re adding the betta to should have a gentle filter, since betta fish are from non-flowing waters. You can test your water’s pH levels with a pH monitor. A simple handheld monitor should be available at your local pet store. Aquarium tank thermometers are useful for monitoring the temperature in your betta fish tank. Keep one in the tank so you can check the temperature quickly at all times. Do not keep your betta in a tank without a filter unless you have the time and energy necessary to perform frequent, high-volume water changes. Do not use distilled water. Betta fish need water with vitamins and minerals that are unavailable in distilled water.


















Comments
0 comment