
views
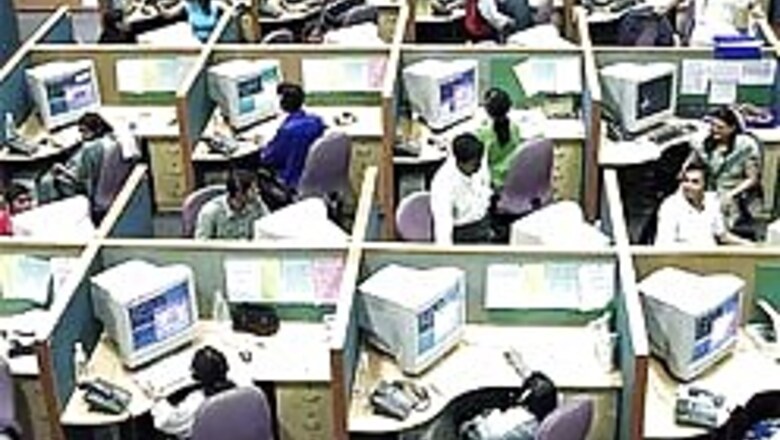
New Delhi: The services sector has emerged as the main employer of female workers in urban India, accounting for the highest proportion of employment at 36 per cent of the total employed. Manufacturing sector followed (at 28 per cent) and agriculture sector (at 18 per cent).
As for the urban males, trade, hotel and restaurant sectors engage about 28 per cent of the total male work force while manufacturing and services sectors account for nearly 24 and 21 per cent of total employment respectively.
These are the findings of the seventh five-yearly survey on Employment and Unemployment carried out as part of the 61st round National Sample Survey by the National Sample Survey Organisation. The findings of survey, which was carried out between July 2004 and June, 2005, were released here on Friday.
It says about 42 per cent population in the country is employed. The proportion was 44 per cent in rural areas and 37 per cent in the urban areas. About 4 per cent of the rural households and 8 per cent of the urban households had no employed member.
Unemployment
As many as 17 men per 1,000 people are unemployed in rural India today as against 45 in urban India. The unemployment rate was higher among the educated (secondary and above) than that among those whose education level was lower than secondary.
In case of women, the unemployment rates are much higher than that for males. However, the unemployment rates are found to be highest among urban females.
During the period 1999-2000 to 2004-05, the unemployment rate remained almost the same for rural males, while it decreased by 1 percentage point for urban males. The ratio increased by about 1 percentage point for females in both the rural and urban areas.
PAGE_BREAK
The proportion of employed females who were found to be unemployed during the week preceding the date of the survey was 17 per cent in rural India and nearly 9 per cent in urban India. The corresponding percentages for employed males were 4 per cent and 2 per cent respectively.
Urban-rural divide
Meanwhile, the rural India woman has emerged as a more active participant in India’s work force today as compared to her urban counterpart while for man, the ratio is same for both rural and urban areas.
Interestingly, it’s not agriculture alone where the rural folks engage themselves today. In fact, the proportion of ‘all’ male workers engaged in agricultural activities have declined from 81 per cent in 1977-78 to 67 per cent in 2004-05.
For female workers, however, the decline was miniscule -- from 88 per cent in 1977-78 to 83 per cent in 2004-05. This explains why as compared to urban females, double the number are employed in rural India.
Gender differences in employment
As for gender differential in the worker population ratio, while 55 per cent males and 33 per cent females are employed in the rural areas, in the urban areas the ratios stood at 55 per cent for males and 17 per cent for females.
In normal population status too, about 56 per cent of rural males and 33 per cent of rural females belonged to the labour force while the corresponding proportions for urban areas were 57 per cent and 18 per cent respectively.
The survey, which covered all the states and Union Territories, was spread over 7,999 villages and 4,602 urban blocks covering 79,306 households in the rural areas and 45,374 households in urban areas.
In another interesting finding, the survey reveals that about 11 per cent of households in both the rural and urban India are today headed by females. Compared to all households, the households headed by females had, on an average, a relatively smaller household size and a much higher sex ratio.
PAGE_BREAK
The survey also says that in as many as 26 per cent of households in rural India and 8 per cent households in urban India, there was not a single member in the age-group of 15 years and above who could read and write a simple message with understanding.
In the rural areas, about 64 per cent of males and 45 per cent of the females were literate during 2004-05. The corresponding proportions for urban areas were 81 per cent and 69 per cent respectively.



















Comments
0 comment