
views
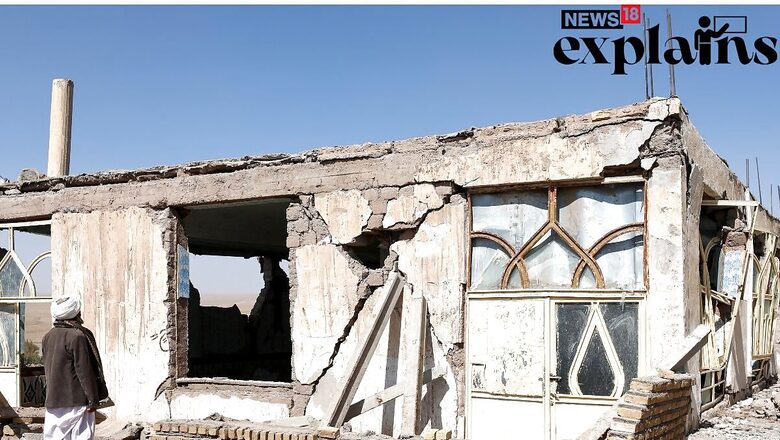
Afghanistan was hit by a second earthquake of magnitude 6.3 on Wednesday days after strong tremors killed more than 2,000 people.
The latest 6.3-magnitude earthquake was about 28 kilometres outside Herat, the capital of Herat province, and 10 kilometres deep, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.
The death toll from the earlier earthquake exceeded 2,000, making it one of the deadliest earthquakes to strike the country in the last two decades.
Though Wednesday’s earthquake killed and injured many, there were no immediate reports of the breakdown of casualties.
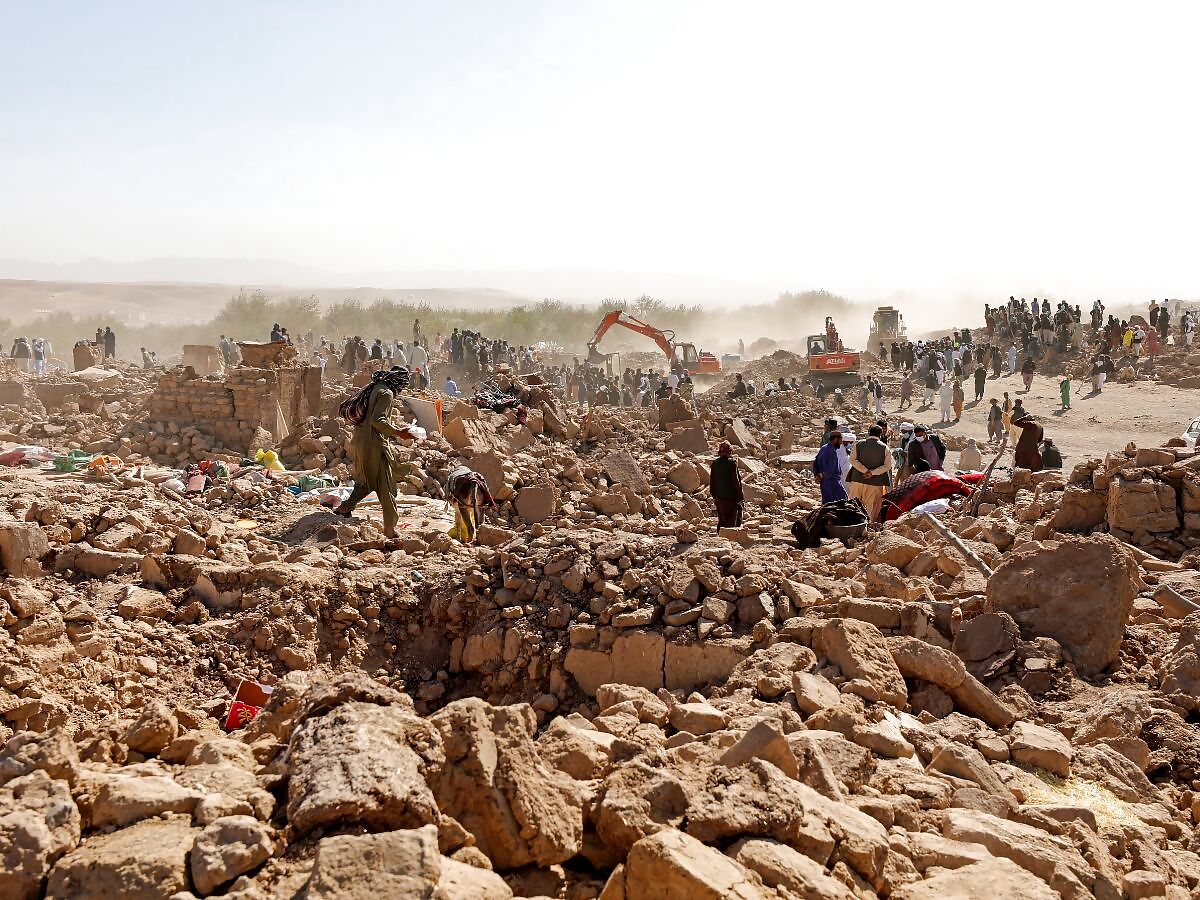
According to a report in the Associated Press, In Naib Rafi village that had about 2,500 residents, people said almost no one was still alive besides men who were working outside when the quake struck.
Afghanistan is already suffering under a humanitarian crisis after the withdrawal of foreign aid following the Taliban’s return to power in 2021.
Why Afghanistan Witnesses Frequent Earthquakes?
Afghanistan is frequently hit by earthquakes, especially in the Hindu Kush Mountain range as it lies near the junction of the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. The country is one of the most seismically active intercontinental regions in the world.
The active faulting is distributed widely across Afghanistan as the northern parts of the country sit within the Afghan-Tajik depression while the Herat Fault stretches across the country to the Iranian border.

Apart from the tectonic plates, the other factor that makes Afghanistan more vulnerable is the wide distribution of active faults across the country.
In June 2022, a powerful earthquake struck a rugged, mountainous region of eastern Afghanistan, flattening stone and mud-brick homes. The quake killed at least 1,000 people and injured about 1,500. In 2021, the country witnessed 219 minor earthquakes with magnitudes of between 1.5 and 4.
Why are earthquakes in Afghanistan More damaging?
The earthquakes in Afghanistan are more damaging though Japan and South American countries have more earthquakes because of the construction styles of the houses and buildings.
The country follows the traditional method of construction and the houses in rural areas are mud built around wooden support poles and are not earthquake-resistant.
The houses and buildings consist of a thick flat or domed roof of dried mud supported by timber, sitting on walls of mud brick or of stone blocks cemented with dried mud.
Moreover, a lot of damage from earthquakes in Afghanistan’s mountains also comes from the landslides they cause. The landslides flatten houses in mountain villages and also block up rivers, causing widespread flooding, according to BBC.
Recent Earthquakes in Afghanistan
Here is a list of some major earthquakes that struck Afghanistan in the past two decades:
- Badakhshan 2023: A magnitude 6.5 earthquake struck the northeastern province of Badakhshan, 40 km southeast of Jurm village, killing at least 13 people.
- Kunar 2022: in September last year, the tremors hit Kunar province in Afghanistan killing eight people.
- Paktika 2022: A 6.1 magnitude earthquake killed 1,036 people in the eastern province of Paktika causing widespread damage and forcing Afghanistan to appeal for international aid.
- Hindu Kush 2015: A 7.5 magnitude earthquake, one of the largest in Afghanistan’s recorded history, killed 399 people in Afghanistan and neighbours Pakistan and India.
- Hindu Kush 2002: Twin earthquakes in the Hindu Kush in March 2002 killed a total of 1,100.
(With inputs from Reuters)



















Comments
0 comment