
views
X
Research source
Raising Hemoglobin with Diet Change
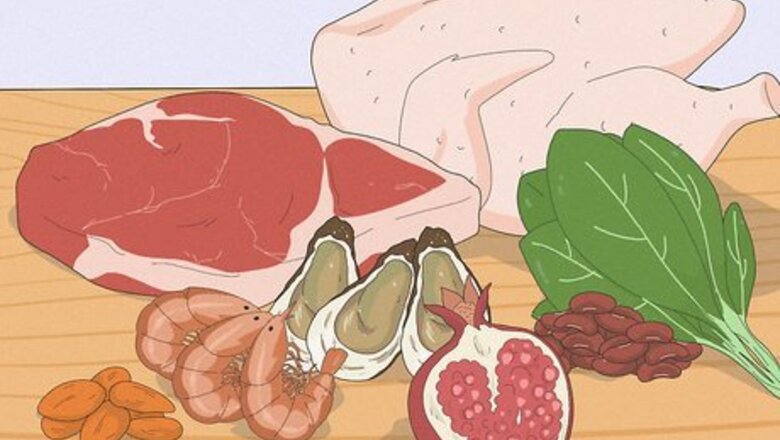
Eat iron-rich foods. Iron is an important element in hemoglobin production—it helps your red blood cells deliver oxygen to the rest of your cells. If you’re suffering from low hemoglobin count, increase your consumption of iron-rich foods such as: Seafood like shrimp and clams Lean meats, like chicken and beef Tofu Eggs Green leafy vegetables like spinach Certain fruits like pineapple, apples, and pomegranates Beans and other legumes Nuts like almonds. These should be eaten with precaution to avoid having an allergic reaction.

Increase your intake of vitamin C. Vitamin C can facilitate iron absorption in the body. It can be acquired by consuming these fruits and vegetables: Oranges Mangoes Tangerines Strawberries Cabbage Broccoli Peppers Spinach.
Eat more folic acid-rich foods. Folic acids are vital in red blood cell production. Foods that are rich in folic acids include: Seeds Peanuts Wheat germ Sprouts Broccoli Nuts If your diet also includes lots of vitamin C, it is advised to eat a little more folic acid since Vitamin C makes the body excrete folic acid.
Eat whole grains. Cereals, pastas and breads made from whole grains are enriched with iron. As we discussed, iron is a main component in the production of hemoglobin (the blood needs it to form the proteins). Eating these foods can up your iron levels, in turn upping your hemoglobin level. Stay away from white breads, cereals, and pastas. These have had their nutrients processed out of them, also resulting in them losing their color. They offer little nutritional benefit and are often full of simple carbohydrates, or sugars.

Avoid foods that block iron. Avoid iron blockers – these are food items that can block the body’s ability to absorb iron. Examples of iron-blocking foods and substances are: Parsley Coffee Milk Tea Colas Over the counter antacids Fiber and calcium-rich foods Alcohol like wine and beer

Try to eat less gluten. Gluten is a form of protein that can be obtained from grains. For some individuals with gluten-sensitive enteropathy, the intake of foods containing gluten can damage the lining of the small intestine, which in turn can cause impairment in nutrient absorption including calcium, fat, folate and iron. Nowadays, having a gluten-free diet doesn't have to be inconvenient. Many restaurants easily accommodate those that need to eat gluten-free and gluten is also labeled on many products in grocery stores.
Raising Hemoglobin with Natural Remedies

Use withania and ashwagandha supplements to boost hemoglobin levels. While still being researched and having no high-quality evidence currently, usage of these herbs may increase hemoglobin levels. They are used in ayurvedic medicine to treat iron deficiency anemia. Talk to your doctor about these supplements and how much is appropriate for you. Avoid using it while pregnant or breastfeeding. This may interact with several other medications.

Take nettle leaf to get a rich source of iron. Nettle leaf is an herb that can be a rich source of iron and is historically used to treat arthritis. Iron plays an important role in producing and absorbing hemoglobin. The more iron you take, the more hemoglobin will be produced. Nettle leaf is available in many vitamin and supplement stores and online. It is available as an oil, in capsule form, and even as a tea.
Try dong quai supplements. While there is no quality data available, some small studies reveal that the consumption of dong quai can restore hemoglobin levels to a nearly normal range. It is traditionally utilized to treat premenstrual syndrome (PMS), menstrual symptoms, menstrual cramps, constipation and anemia. The cobalt in dong quai is thought to increase the hemoglobin content of your blood. Dong quai is mostly available in capsule form, though it can also be used as an oil you can mix into your drinks. It is available at supplement stores, some pharmacies, and online. Avoid using while pregnant or breastfeeding.
Consider trying chitosan. A small study demonstrated that patients with kidney failure that were given 45 mg of chitosan showed relatively reduced cholesterol levels and increased hemoglobin levels. Talk to your doctor about this natural remedy and if it's right for you. Chitosan is available online and in special vitamin supplement stores. For the record, it's pronounced KITE-uh-san. Chitosan should not be taken by people who are allergic to shellfish or mushrooms or by people who are taking Warfarin.
Seeking Medical Help to Raise Hemoglobin
Talk to your doctor about taking supplements to increase your hemoglobin count. Some patients are advised to take prescribed or over the counter medications or supplements to augment their levels of hemoglobin. However, be sure to only take supplements under your doctor's supervision, as they'll need to monitor your complete blood count and iron, ferritin, and transferrin levels over the course of treatment. Supplements may include: 20-25mg of iron per day. This stimulates the production of hematin. 400mcg of folic acid per day. This is taken to increase the production of red blood cells which transport hemoglobin. 50-100mcg per day of vitamin B6. This functions also to increase red blood cell production. 500-1000mg per day of vitamin B12. It is prescribed to enhance red blood cell count. 1000mg per day of vitamin C. It is administered for red blood cell production as well.
Talk to your doctor about getting erythropoietin injections. Erythropoietin is a hormone manufactured by the kidneys to promote the development of red blood cells by the bone marrow. Once the kidney cells sense that the oxygen level in the blood is too low it produces and releases erythropoietin to stimulate the bone marrow to generate more red blood cells. The increase in red blood cell count can also enhance the capacity of blood to carry oxygen. In general, erythropoietin functions mainly to encourage the production of red blood cells and instigate the synthesis of hemoglobin (a component of the red blood cells that are in charge in transporting oxygen) . Erythropoietin is administered either through the veins or via subcutaneous (external, fatty portion of the legs and thighs) injection.
Consider getting a blood transfusion if your hemoglobin levels are very low. Blood transfusions are sometimes recommended by health care providers to improve hemoglobin count. Prior to transfusion, safety precautions are taken to ensure the quality and compatibility of blood. It is tested for signs of contamination which can cause adverse reactions to patients. Donated blood can contain infectious components for HIV/AIDS and hepatitis so proper screening is very important. After a thorough examination, the blood transfusion is given. It is administered through a central venous catheter or intravenous line in the arm over several hours. The patient is then watched carefully for any untoward signs of blood transfusion such as difficulty of breathing, itchiness or rashes and an increase in body temperature.

















Comments
0 comment