views
Installing Python 3
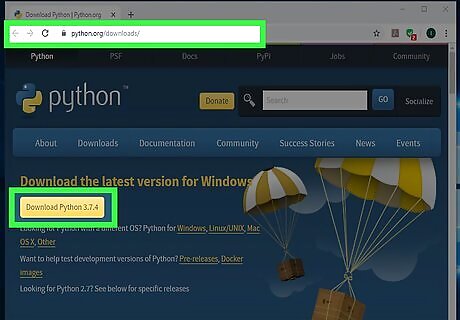
Go to https://www.python.org/downloads. The most recent version of Python will always appear on the "Download" button near the top of the page. If you want to use Python 2, see the "Installing Python 2" method.
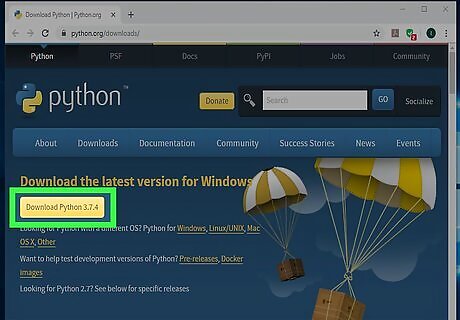
Click Download Python
Run the installer. You can do so by double-clicking python-
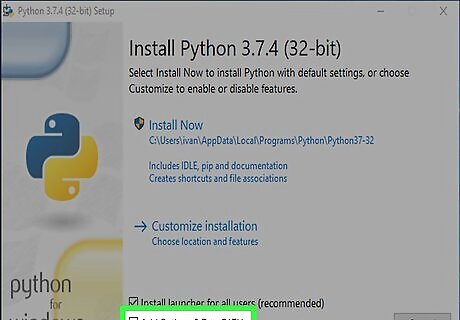
Check the box next to "Add Python
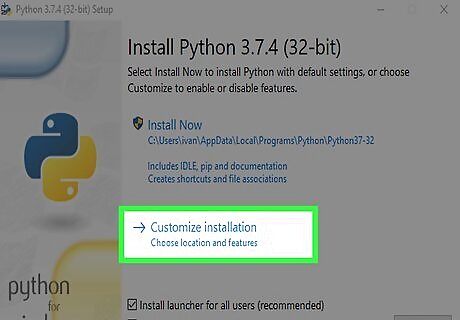
Click Customize installation. It's the second blue link on the window.
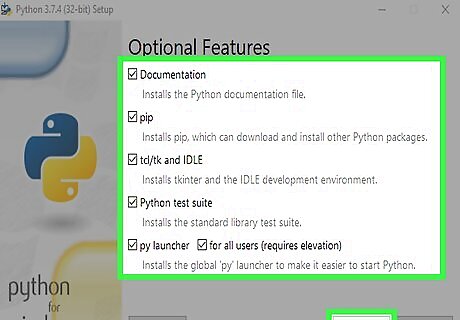
Review the installation options and click Next. All Python's features are selected by default. Unless you have a specific need to skip installing any part of this package, just leave these settings alone.
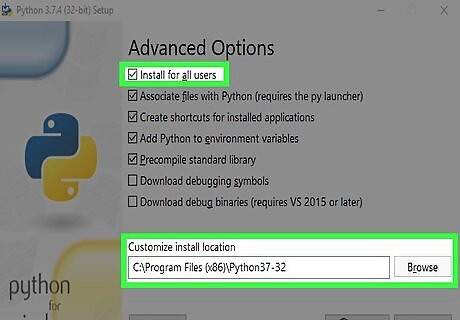
Check the box next to "Install for all users."" If you're a system administrator, this option ensures that other users on this computer can use Python. This also changes the installation location to the Program Files\(x86)\Python(version) instead of your personal library.
If you didn't have the option to select "Add Python
Click Install. It's at the bottom of the window.
Click Yes to confirm. This installs Python on your PC. Once the installation is complete, you'll see a "Setup was successful" window—don't close it yet.
Click Disable path length limit. It's toward the bottom of the "Setup was successful" window. This final step ensures that Python (and other apps) can use paths more than 260 characters in length.
Click Yes to confirm. Python is now installed and ready to use.
Click Close to exit the installer.
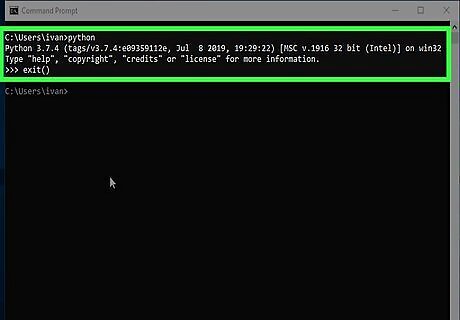
Test your Python installation. Here's how to ensure the path is set up properly: Type cmd into the Windows search bar and press ↵ Enter. Type python and press ↵ Enter. You should see >>> at the beginning of the current line. This means Python is working and the path is set correctly. If you see an error that says "python is not recognized as an internal or external command," see the "Adding the Python Path to Windows" method. Type exit() to return to the command prompt.
Installing Python 2
Be aware that Python 2.x is no longer being maintained, and is not recommended to download or program with. And if you're new, you should download the newest version and learn the newest features of the Python language.
Go to https://www.python.org/downloads in a web browser. Use this method if you want to write code in Python 2 instead of (or in addition to) Python 3 in Windows.
Scroll down and click a Python 2 version. The versions appear under the "Looking for a specific release?" header. If you don't know which version of Python 2 to install, just click the first version beginning with "2." In the list. This ensures you're using the most recently-updated version.
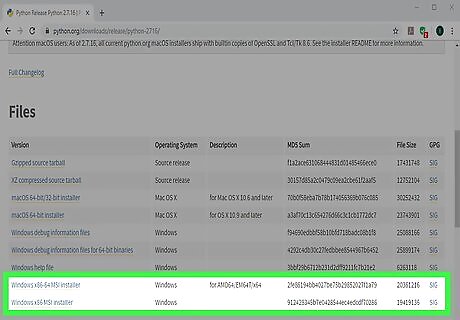
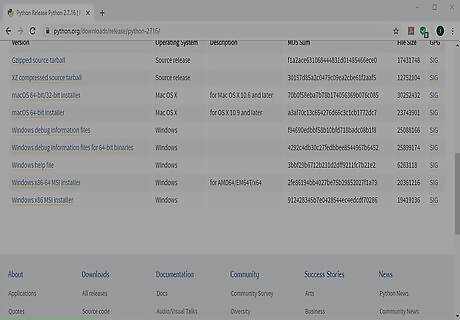
Scroll down and select an installer. This downloads the installer to your computer, though you may have to click Save to start the download. If you have a 64-bit computer, select Windows x86-64 MSI installer. If you're using a 32-bit computer, select Windows x86 MSI installer.
Run the Python installer. You can do this by double-clicking python-(version).msi in your Downloads folder.
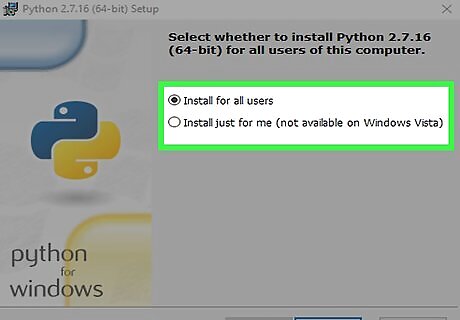
Select an option for installing. If you want other users of this PC to use Python, select Install for all users. If not, select Install for just me.
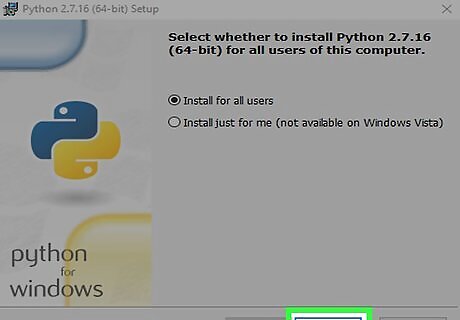
Click Next. It's at the bottom-right corner.
Select an install directory (optional). The default directory is fine for most people, but you can change it if you wish by selecting a different folder from the menu.
Click Next.

Scroll down to the bottom of the "Customize Python" features list. You should see an option called "Add python.exe to Path." It probably has an "X" on its corresponding button. If you don't see this option, see this method after installing Python.
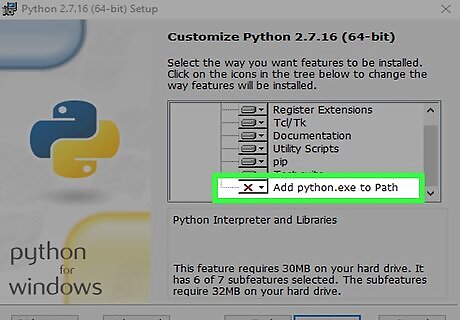
Click the X button next to "Add python.exe to Path." A menu will expand.
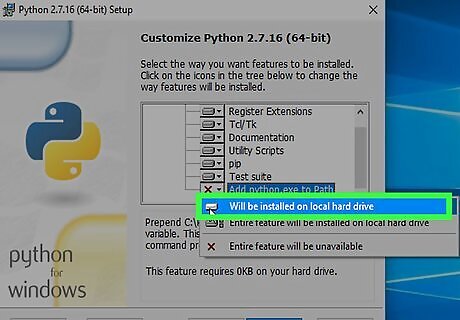
Click Will be installed on local hard drive. This ensures you can run Python commands from anywhere without having to type the full path to Python.
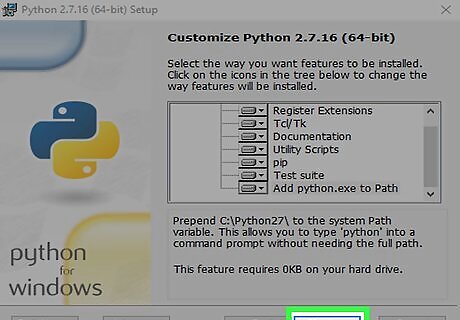
Click Next. A security pop-up will appear on most systems at this point.
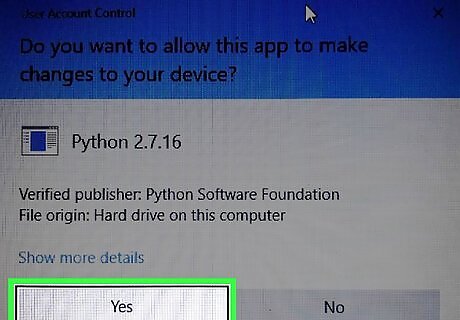
Click Yes to continue. This installs Python 2 on the PC. In a few moments, you'll see a window that says "Complete the Python Installer."
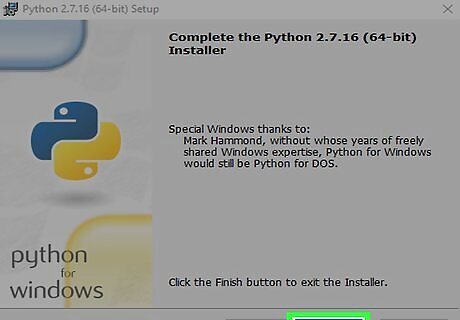
Click Finish on the installer. Python is now installed.
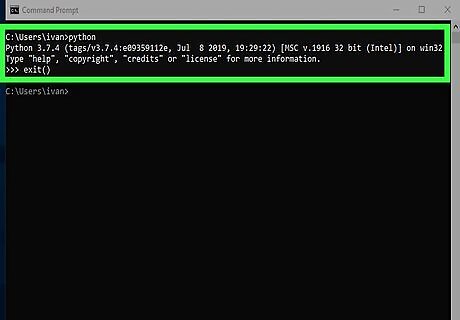
Test your Python installation. Here's how to ensure the path is set up properly: Type cmd into the Windows search bar and press ↵ Enter. Type python and press ↵ Enter. You should see >>> at the beginning of the current line. This means Python is working and the path is set correctly. If you see an error that says "python is not recognized as an internal or external command," see the "Adding the Python Path to Windows" method. Type exit() to return to the command prompt.
Adding the Python Path to Windows
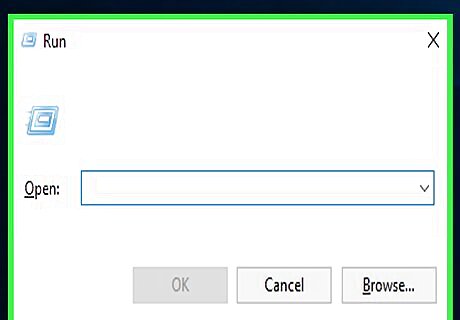
Press ⊞ Win+R to open the Run dialog. Use this method if you're installing an older version or see the "python is not recognized as an internal or external command" error when trying to use Python.
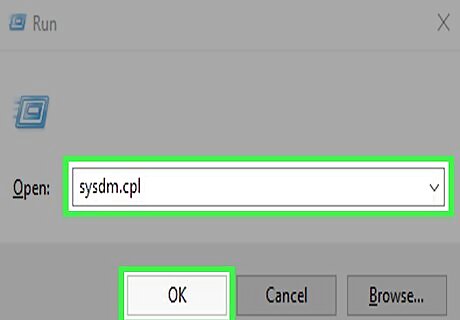
Type sysdm.cpl and click OK. This opens the System Properties dialog.
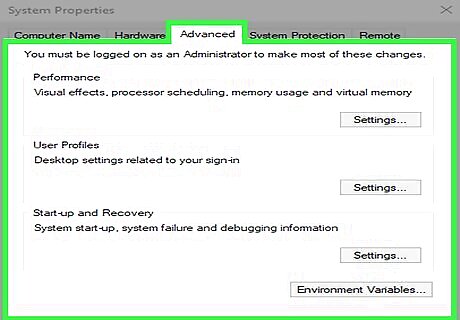
Click the Advanced tab. It's at the top of the window.
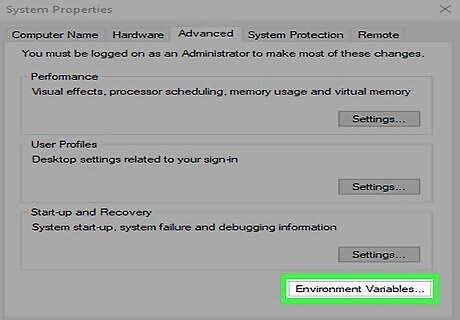
Click Evironment Variables. It's near the bottom of the window.
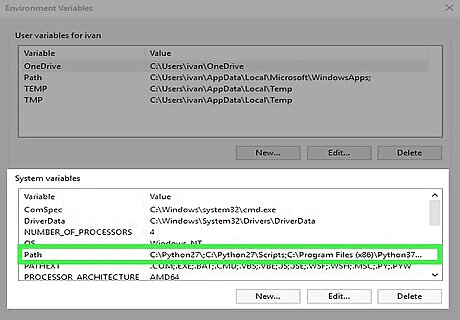
Select the Path variable under "System variables." This is in the second group of variables (not the "User variables" group on top).
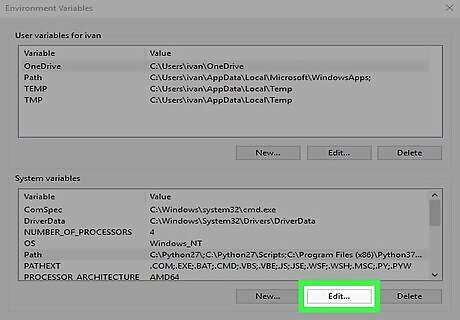
Click Edit. It's at the bottom of the window.
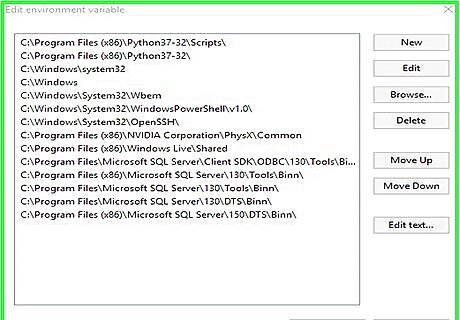
Edit the variables on Windows Vista and earlier. If you're using Windows 10, 8, or 7, skip to the next step. If you're using XP or Vista: Click inside the "Variable value" box to delete the selected text. Scroll all the way to the end of the text already in the "Variable value" box. Type a semicolon ; at the end of the text (no spaces). Type the full path to Python (e.g., C:\Python27) right after the semicolon. Type a semicolon ; at the end of what you just typed (no spaces). Type the full path again, but add \Scripts to the end. Example: C:\Python27\Scripts;C:\Python27\Scripts. Click OK until you've closed all windows, and then restart your PC. No need to continue with this method.
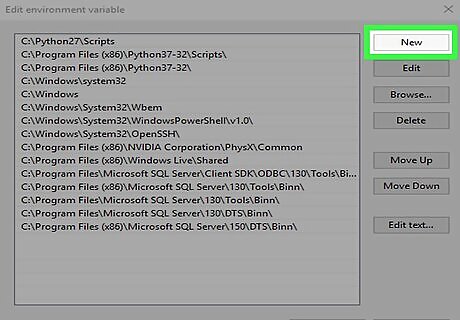
Click New. It's the first button near the top-right corner of the window.
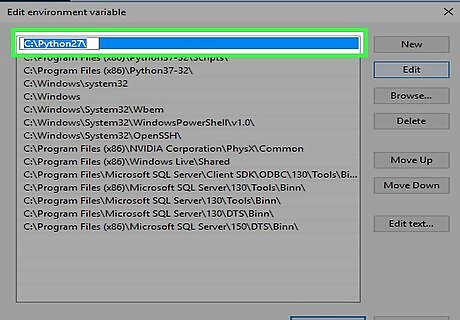
Enter the full path to Python. For example, if Python is installed to C:\Python27, type that into the field.

Press ↵ Enter. Now you'll have to enter just one more path.
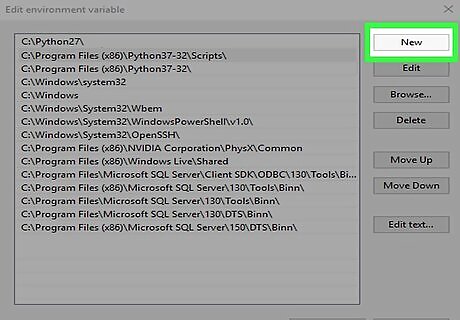
Click New again.
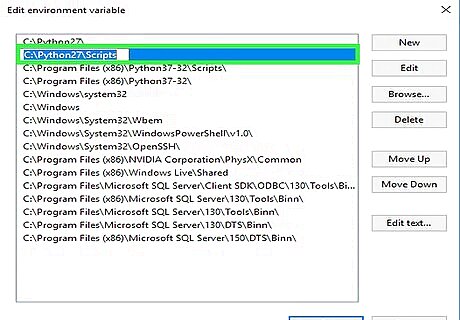
Enter the full path to the Python "Scripts" directory. This is the same path as you typed before, except you'll be adding \Scripts to the end. For example, C:\Python27\Scripts.

Press ↵ Enter. Your new variables are saved.
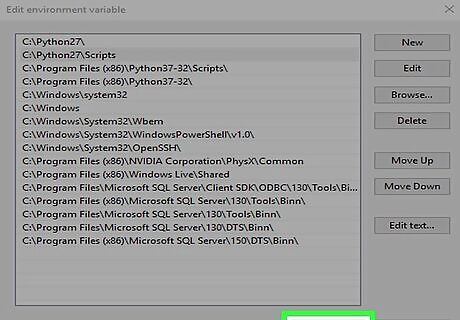
Click OK and then OK again. You should now run Python from the command line by typing python.


















Comments
0 comment