views
Eating to Boost Lymphocytes
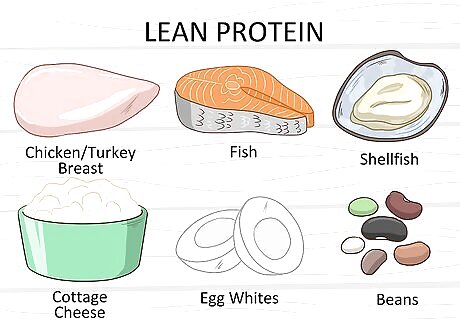
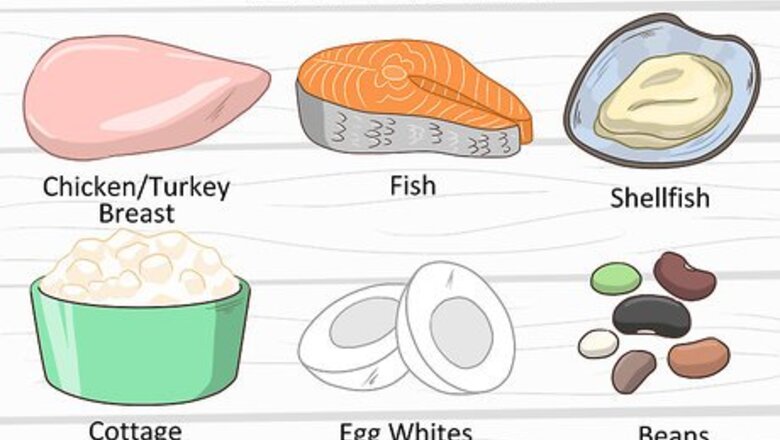
Eat lean protein. Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids, which your body needs to produce white blood cells. When the body doesn't get enough protein, it produces fewer white blood cells. This means you can boost your lymphocyte production by eating the right amount of protein. Great options for lean protein include chicken or turkey breasts without the skin, fish, shellfish, cottage cheese, egg whites, and beans. To find out how much protein you should eat, multiply your bodyweight in kilograms by .8. This provides you with the minimum grams of protein you should eat per day. Your body weight is the maximum grams of protein you should eat per day. You can convert your weight from pounds to kilograms by multiplying your weight by .45. Alternatively, you can use an online calculator.

Avoid foods that are high in saturated and trans fat. Bad fats like saturated and trans fat thicken your lymphocytes, making them less effective. Reducing your saturated and trans fat consumption can improve your immune system. Additionally, you should choose mono- and poly-unsaturated fats over trans fats or saturated fats. Replace saturated and trans fat with healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids, which can actually increase lymphocytes. Keep your fat consumption to 30% of your calories, with just 5 to 10% of that being saturated fat. You can avoid trans fats by steering clear of hydrogenated oils, commercial baked goods, fried foods, fast food, non-dairy creamer, and margarine.
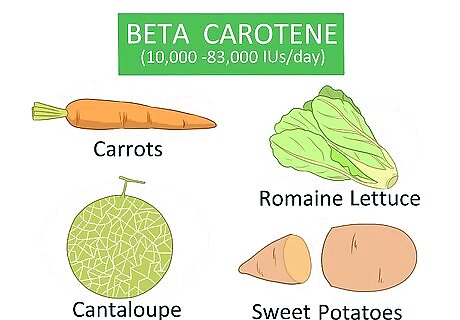
Eat foods that contain beta carotene. Beta carotene supports your immune system by boosting your production of lymphocytes. As a bonus, it also helps protect your body from cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Most doctors recommend between 10,000 and 83,000 IUs per day. If you eat 5 or more servings of vegetables each day, you should reach this daily goal. Beta carotene is a fat-soluble vitamin, so you should eat it with at least 3 grams (0.11 oz) of fat to ensure absorption. For example, you could dip carrots in hummus or eat a salad with a low-fat dressing, such as olive oil mixed with balsamic vinegar. Beta carotene from food is processed differently than a supplement, so you won't get the same benefits. In supplement form, it may cause harm to some people, such as smokers. You can find beta carotene in sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, romaine lettuce, butternut squash, cantaloupe, and dried apricots.
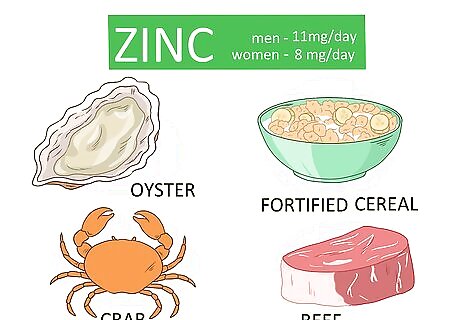
Eat foods that contain zinc. Zinc helps increase your T-cell and natural killer cells, strengthening your immune system. Your body requires zinc to make lymphocytes, so make sure that you reach your recommended daily requirements. Men should aim to eat at least 11 mg of zinc per day, while women should eat at least 8 mg. Women who are pregnant should eat at least 11 mg of zinc per day, while lactating women should eat 12 mg. Good food choices include oysters, fortified cereals, crab, beef, dark meat turkey, and beans.
Season your food with garlic. Garlic boosts your white cell production, increasing natural killer cells. As an added benefit, it acts as an antioxidant, which supports your health. Garlic also helps prevent cardiovascular disease by preventing blood clots. You can buy dried, powdered garlic, or you can use fresh cloves.

Sip green tea every day. Green tea supports your immune system, helps fight against viruses that can deplete your white blood cells, and may help your body increase white blood cells. It's a great alternative to other beverages that may be taxing to your system, like sugary drinks.
Using Vitamins and Supplements

Take vitamin C. Vitamin C increases your body's production of white blood cells, including lymphocytes. While you can eat your vitamin C, it's also readily available as a supplement. Since your body does not make or store vitamin C, you should eat sources of the nutrient every day. When you take vitamin C, your body uses what it needs and excretes the rest. This means that you would need to take the vitamin C every day. Always talk to your doctor before taking any vitamins or supplements. Supplements can sometimes interfere with the absorption of other medications, vitamins, or minerals. Supplements can be expensive. If you are eating fruits and vegetables to get your vitamin C every day, you may not need a vitamin C supplement.
Include vitamin D in your diet. Not getting enough vitamin D can weaken your immune system and lower your lymphocytes. Make sure you're getting at least 600 IU of vitamin D every day. You may not be able to get all of your vitamin D from diet alone. Talk to your doctor about taking vitamin D supplements.
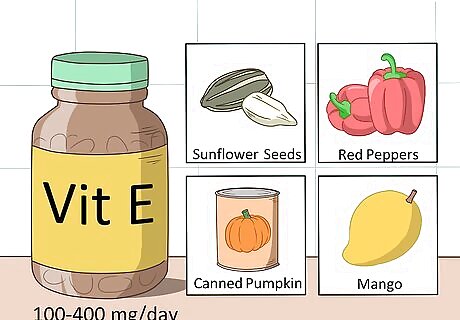
Try vitamin E. Vitamin E supports your body's production of B-cells and natural killer cells. To get the benefit, you will need to take between 100 to 400 milligrams per day. People who are generally healthy need less, while people who are less healthy may require more. Since vitamin E is a fat soluble vitamin, you should take it with a meal that contains at least 3 grams (0.11 oz) of fat. If you want to eat your vitamin E, great options include sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, safflower oil, beet greens, canned pumpkin, red peppers, asparagus, collard greens, mango, avocado, and peanut butter. You can find vitamin E supplements at drug stores, vitamin stores, and online.

Add selenium. Selenium helps your body produce more white blood cells. Since you may not get it easily in your diet, selenium can be taken as a supplement. When taken along with zinc, both minerals are more effective at supporting your immune function. The recommended daily allowance of selenium for adults is 55 mcg per day. If you are pregnant, you should aim for 60 mcg, while nursing women should consume 70 mcg. You can also eat your selenium if you like to consume a lot of seafood. It's present in foods like oysters, crabs, and tuna.
Making Lifestyle Changes
Talk to your doctor if you have a serious health issue. Low lymphocytes have many causes, many of them temporary. For example, viral infections, severe bacterial infections, and certain antibiotics can all temporarily lower your lymphocyte count. Some causes, however, are serious. These include certain cancers, autoimmune diseases, and disorders that reduce bone marrow function. If you suspect a serious issue, your doctor can make a proper diagnosis and create a treatment plan. Better treatment options may be available to you, such as a bone marrow transplant.

Sleep the recommended number of hours each night. Adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep to be fully rested. Teens may need up to 10 hours per night, while children may need up to 13. Being tired weakens your immune system by reducing your number of white blood cells. Getting enough sleep supports your immune system.

Incorporate stress-reduction activities into your day. Stress makes your body work harder, which weakens your immune system. It also causes your body to secrete hormones like cortisol that stay in your blood. You become more susceptible to illness, which lowers your white blood count. To avoid stress, add stress-reduction activities to your day. Try yoga. Do meditation. Go for a walk in nature. Try deep breathing. Engage in a hobby.
Stop smoking. Smoking weakens your immune system, including your white blood cells. Your body will not be able to produce or maintain high levels of lymphocytes.
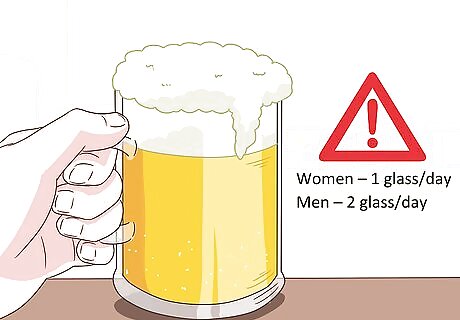
Limit alcohol consumption. Moderate drinking won't hurt your immune system, but excessive drinking can take a toll on your body. It stresses your system, which prevents it from producing enough white blood cells. Women should limit themselves to 1 glass of alcohol per day, while men should stick to 2.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being underweight or overweight can stress your body's production of white blood cells. Your body may not produce as many white blood cells, and the ones you do have won't function as well. Maintain your weight by eating a balanced diet and getting regular exercise. Eat lots of vegetables. Include a small serving of lean protein at each meal. Eat 2 to 3 servings of fruit per day. Drink plenty of water. Limit sugars and unhealthy fats.

Exercise most days. Regular exercise supports your immune system by improving your circulation, which allows the lymphocytes to do their job. Try to exercise for 30 minutes 5 times a week. You should pick an activity (or activities) that you really enjoy. Good options include walking, dancing, biking, hiking, swimming, running, team sports, and rock climbing.

Wash your hands often. While washing your hands is always good, it is particularly important when you are trying to increase the number of lymphocytes in your body. Washing your hands lowers your risk of getting exposed to things that can cause infections, like bacteria and viruses.



















Comments
0 comment