views
Why are my toes turning outwards?
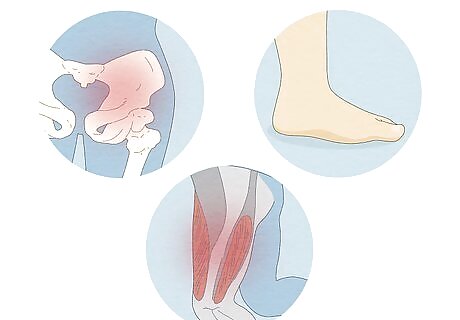
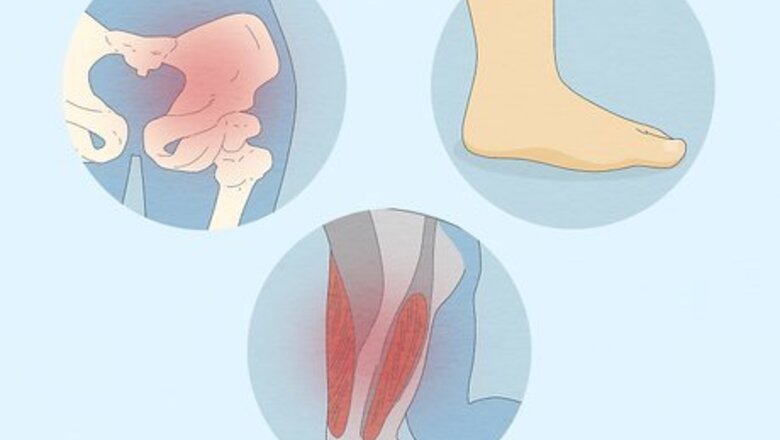
A twisted hip or shin bone is the most common cause. During pregnancy, children’s leg bones have to twist as they grow to fit inside the womb. If the tibia twists outward or if your hips flex upward, then your feet might point out to the sides as well. While some kids grow out of it when they’re toddlers and start walking normally, you may still have out-toeing as an adult. A twisted femur called “femoral retroversion” could also cause out-toeing, but it’s most common in obese children. Lie flat on your back with your legs extended. If your knees point out to the side, then the issue is in your hips. If your knees are straight up and your feet turn to the side, then the issue is in your tibia.
Flat feet also lead to out-toeing. When you don’t have a lot of arch support, your feet are flat against the ground and may lead to posture problems. Since your feet aren’t as stable, your toes will naturally turn outward so you can keep your balance. While flat feet are common in children under 4 and generally improves as you get older, you can develop them as an adult and they could lead to discomfort or out-toeing. Flat feet could also be a symptom of a twisted hip or tibia. You may not have any pain if you have out-toeing from flat feet.
Your hamstrings and glutes could be tight or weak. Both overuse and under-use of your hip and leg muscles can lead to out-toeing. When the muscles in your lower body stiffen or feel weak, they affect your posture and the position of your legs so your feet turn outwards.
How can I straighten my feet?
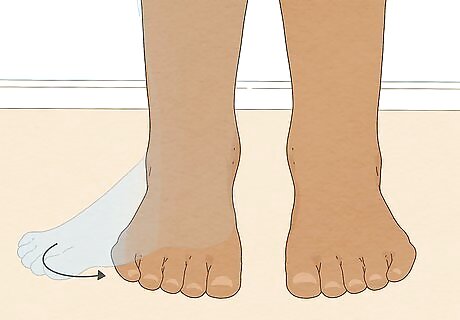
Point your feet forward when you notice they’re misaligned. When you’re standing or walking, take a few seconds to check the position of your feet to see if they’re pointing out. When you notice it, make a conscious effort to point them straight forward. It might feel uncomfortable at first, but it helps retrain your muscles to the proper posture.
Put orthotic inserts inside of your shoes for flat feet. Ask your doctor about getting custom inserts molded for your foot to help support your arches and correct your foot’s position. The orthotics bring the arches of your feet up so your heel turns in and makes your out-toeing less noticeable. Wear the orthotics as often as your doctor recommends so you get used to the new position of your foot. Orthotics will not fully cure out-toeing, but it can help to correct mild conditions. Some experts have found that special shoes or braces aren’t effective or show no differences in treatment.
Stretch and massage your muscles for 20 minutes each day. As you’re working on changing your posture and how you walk, keep your leg muscles limber so you don’t get sore. After stretching, give yourself a self-massage so your legs don’t feel as tight. Some stretches you can try include: Butterfly stretch: Sit up straight and bend your knees. Drop your legs to the side and press the soles of your feet together. Hold onto your feet and slowly lean forward. For a deeper stretch, press down on your thighs. Piriformis stretch: Lie on your back and pull your right knee up toward your chest. Hold onto your knee with your left hand and pull it toward your left shoulder. Hold the stretch for about 30 seconds. Then, pull your left knee toward your right shoulder. Hamstring stretch: Place your heel on a table that’s about waist-height and keep your leg fully extended. Keep your toes pointed up and bend forward at the hips. Hold your stretch for 30 seconds for each leg.
How long does it take to correct duck feet?

It may take a few years to retrain your posture. Since the changes are usually gradual, it’s hard to notice when out-toeing fully improves. Record a video of you walking normally when you first start your recovery. Throughout the year, keep working on training your posture and correcting the positions of your feet. After a year, record another video to see if you’ve improved. If you don’t see any changes, talk to your doctor about what you can do for the next steps.
You may need surgery if out-toeing doesn’t improve on its own. If you’re feeling a lot of stress or pain in your knees, then it might be time for surgery. Usually, your doctor will perform an osteotomy, which is when they cut part of your leg bones to help realign them in the right position. Often times, the procedure is minimally invasive and you’ll recover quickly. For more severe conditions, you may have wires, plates, or screws inserted to hold your leg in position while it heals.
Is duck walking bad for your knees?
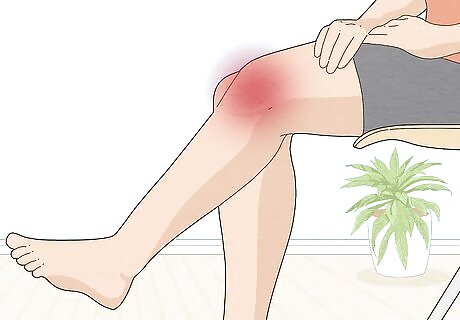
It can cause stress on your knees and lead to joint pain.. When you’re a child, you’ll usually stop out-toeing as your legs get stronger. However, it can start feeling a little more painful once you’re older than 10. If you continue out-toeing, you might start feeling pain in your knees or ankles and could start developing arthritis. Out-toeing can also make it difficult or painful to run, bike, or play sports.
When should I worry about out-toeing?
Seek treatment if out-toeing causes pain or limits your movements. For many cases, out-toeing goes away as you get older, but it may be persistent. If you have trouble walking, limp, or have one foot that turns out more than the other, reach out to your doctor or a physical therapist. They’ll be able to diagnose the cause of your condition and offer up the best treatment for it. Your doctor will usually give you a physical to check your range of motion and do a neurological exam to check for nerve and muscle function. They may order x-rays if they find anything concerning.
Is out-toeing genetic?
Some cases of out-toeing might run in the family. The most common genetic cases happen when you have a twisted tibia or femur. While it’s still unclear why some people develop out-toeing and others don’t, some doctors think it might be hereditary. If your parents or relatives had out-toeing when they were younger, there’s a chance that they’ve passed it on to you as well.



















Comments
0 comment