views
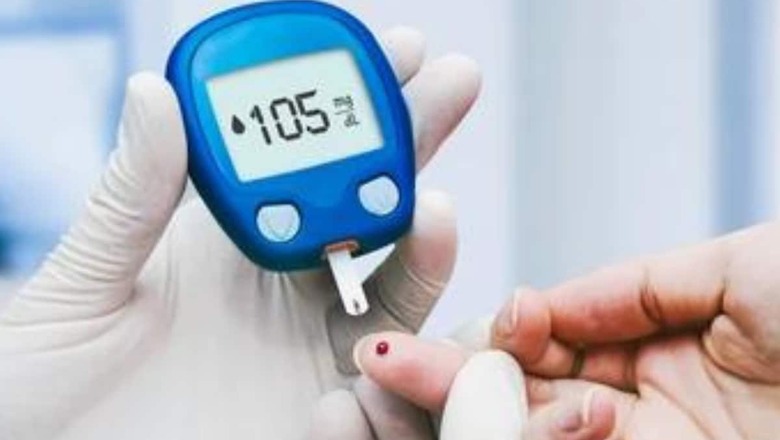
Diabetes in young adults, people who are less than 30 years of age, has been on the rise in last two decades. Until recently, the common type of diabetes in children and young was Type 1 DM. Type 1 diabetes is a condition where the pancreas cannot produce sufficient insulin to lower blood sugar and people living with Type 1 DM must inject insulin multiple times a day.
Type 2 DM can occur when insulin is not working correctly (Insulin resistance). The chance of developing type 2 diabetes increases as people get older, but now it is becoming more common in children and young individuals Apart from Type 1 and Type 2 DM there are a range of less common types of diabetes, which are important particularly in young. These include Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY), Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA), and diabetes due to certain medications or hormonal imbalances. Treatment might differ in these types and thus diagnosing it correctly is important.
What are the risk factors and causes associated with young-age diabetes?
“Your chances of developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2 DM) depend on a combination of various risk factors rather than one single risk factor. Certain risk factors like family history, age, race, or ethnicity, can’t be changed, however you may be able to avoid some risk factors by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and being physically active. It is important to know that obesity and sedentary lifestyle are the major risk factors for type 2 DM. If you have obesity, you’re about six times more likely to develop type 2 DM than those at a healthy weight. For other types of DM like MODY or LADA genetic factors play an important role,” says Dr Piyush Lodha, Endocrinologist, Diabetologist, General Physician, Ruby Hall Clinic, Pune.
How does young-age diabetes differ from diabetes in adults?
Various types of Diabetes will have clinical implications on treatment options. “For example, people living with type 1 diabetes or LADA must inject insulin multiple times a day, while type 2 diabetes can manage their condition with lifestyle modification and oral medications. Other less common types are to be treated based on the type of Diabetes,” adds Dr Lodha.
Long-term problems from type 2 diabetes might include heart disease, kidney, eye, or nerve damage. And young adults with type 2 diabetes are more at risk of developing these complications.
What are the common symptoms and warning signs of young-age diabetes?
Diabetes can cause several symptoms in children, such as tiredness, blurred vision, and increased thirst and hunger. “The common symptoms of diabetes are: frequent urination, feeling thirsty, weight loss without trying, uncontrolled appetite, blurry vision, numbness or tingling sensation in feet, feeling tired, and dry skin. Anyone having any of these symptoms should et screened for Diabetes,” describes Dr Lodha.
What are the unique challenges faced by young people with diabetes?
Living with and managing diabetes every day can be a struggle in a Type 1 DM and LADA. “Patient might need to inject multiple insulin doses and monitor his blood glucose levels on a regular basis. Hospitalization rates associated with severe hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, especially ketoacidosis, are greater in Type 1 DM,” explains Dr Lodha.
On the other hand, Type 2 DM cases need good lifestyle practices that should be sustainable and achievable. Individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at younger ages often have more severe disease and are more likely to develop diabetes complications earlier and have more advanced complications.
What are the psychological and emotional aspects of living with young age diabetes?
A young individual, newly diagnosed with diabetes can have various reactions and emotions including shock, denial, sadness and fear. “Proper Diabetes education program and support helps subside these reactions. It is generally known that family functioning has a significant role in diabetes adaption,” states Dr Lodha. Diabetes is a risk factor for developing psychological problems, which include
- Depressive disorders,
- Anxiety disorders
- Behavior disorders
- Fear of hypoglycemia is a important barrier for Diabetes management.
- Body image concerns and eating disorders
Promoting parent child collaboration and team management are the simple strategies which can help solve these challenges.



















Comments
0 comment